Figure 4.
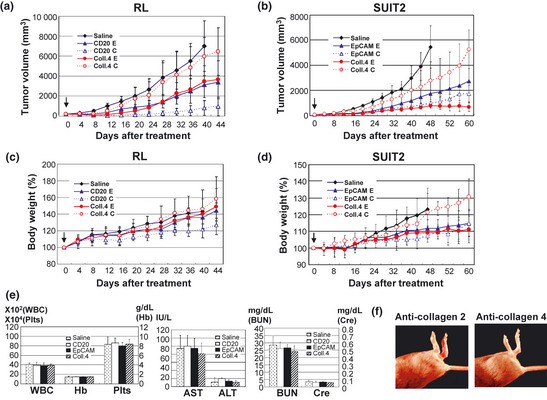
Antitumor effects and toxicities of immunoconjugates‐PEG‐SN‐38 in the combinations of anti‐cell or anti‐stroma targeting, carbonate‐bond or ester‐bond. (a,b) Anti‐tumor activities and (c,d) percent changes of body weight were examined. In animal models of RL (a,c) and SUIT2 (b,d), the six types of immunoconjugates (combined anti‐CD20 monoclonal antibody (mAb) =CD20, anti‐EpCAM mAb=EpCAM or anti‐collagen 4 mAb=Coll.4 and ester‐bond=E or carbamate‐bond=C), or saline as control, were administered once at an equivalent SN‐38 dose of 3 mg/kg to separate groups of mice (n = 5) by intravenous bolus injection to the mice on day 0. Arrows indicate day of administration and the curves illustrate the effect of treatment on tumor size. P < 0.0001 (saline versus CD20‐E or CD20‐C, CD20‐C versus CD20‐E, Coll.4‐E or Coll.4‐C in RL tumor; saline versus EpCAM‐E, EpCAM‐C or Coll.4‐E, Coll.4‐E versus EpCAM‐C or Coll.4‐C, EpCAM‐C versus Coll.4‐C in SUIT2 tumor), P < 0.001 (Saline versus Coll.4‐E in RL tumor; saline versus Coll.4‐C, Coll.4‐E versus EpCAM‐E in SUIT2 tumor). Bar = standard deviation (SD). (e) Hematological (WBC, Hb and Plts) and biochemical (aspartate aminotransferase [AST], alanine aminotransferase [ALT], blood urea nitrogen [BUN] and creatinine [Cre]) examination were conducted at 7 days after i.v. administration of immunoconjugates via ester‐bond or saline as control. Bar = standard deviation (SD). (f) Anti‐collagen antibody induced arthritis in DBA/1J mice. The arthritis was admitted on day 7 only after the administration of anti‐collagen 2 (left) but not anti‐collagen 4 (right) antibodies.
