Fig. 3.
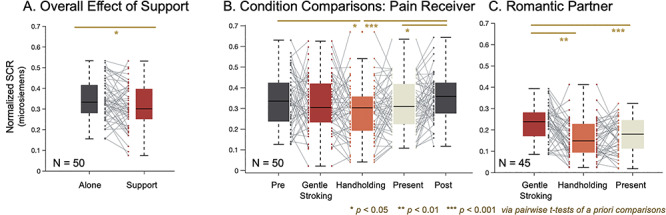
Interpersonal support decreases pain-related physiological responses in women and men. (A) Overall effect of support. Social support reduced pain-related physiological responses across all main participants. (B) Condition comparisons. When conditions were analyzed separately in the pain receiver, we find that this effect is driven by the Handholding condition, where only the Handholding condition is significantly less than the Pre and Post conditions. (C) Romantic partner. Partner SCRs are higher during the Stroking condition than during the passive Present and Handholding conditions.
