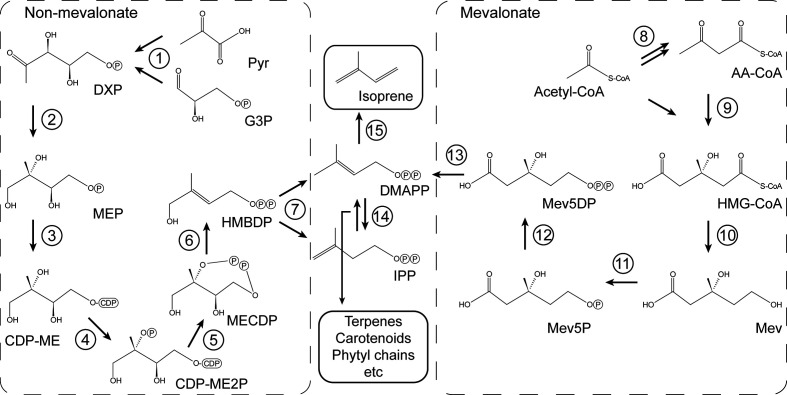
Fig. 1.
Non-mevalonate (methylerythritol 4-phosphate, MEP) and mevalonate (MVA) pathways for biosynthesis of isoprenoid precursors isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate. Pyr, pyruvate; G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; DXP, 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate; MEP, 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate; CDP-ME, 4-(cytidine 5′-diphospho)−2-C-methyl-d-erythritol; CDP-ME2P, 2-phospho-4-(cytidine 5′-diphospho)−2-C-methyl-d-erythritol; MECDP, 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate; HMBDP, 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-butenyl 4-diphosphate; AA-CoA, acetoacetyl-CoA; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA; Mev, mevalonate; Mev5P, mevalonate 5-phosphate; Mev5DP, mevalonate 5-diphosphate; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; DMAPP, dimethylallyl diphosphate. Enzymes: 1, DXP synthase; 2, DXP reductoisomerase; 3, MEP cytidylyltransferase; 4, CDP-ME kinase; 5, MECDP synthase; 6, HMBPP synthase; 7, HMBPP reductase; 8, acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase; 9, HMG-CoA synthase; 10, HMG-CoA reductase; 11, mevalonate kinase; 12, phosphomevalonate kinase; 13, mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase; 14, isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase; 15, isoprene synthase.