Fig 3. S-Stage pooling example.
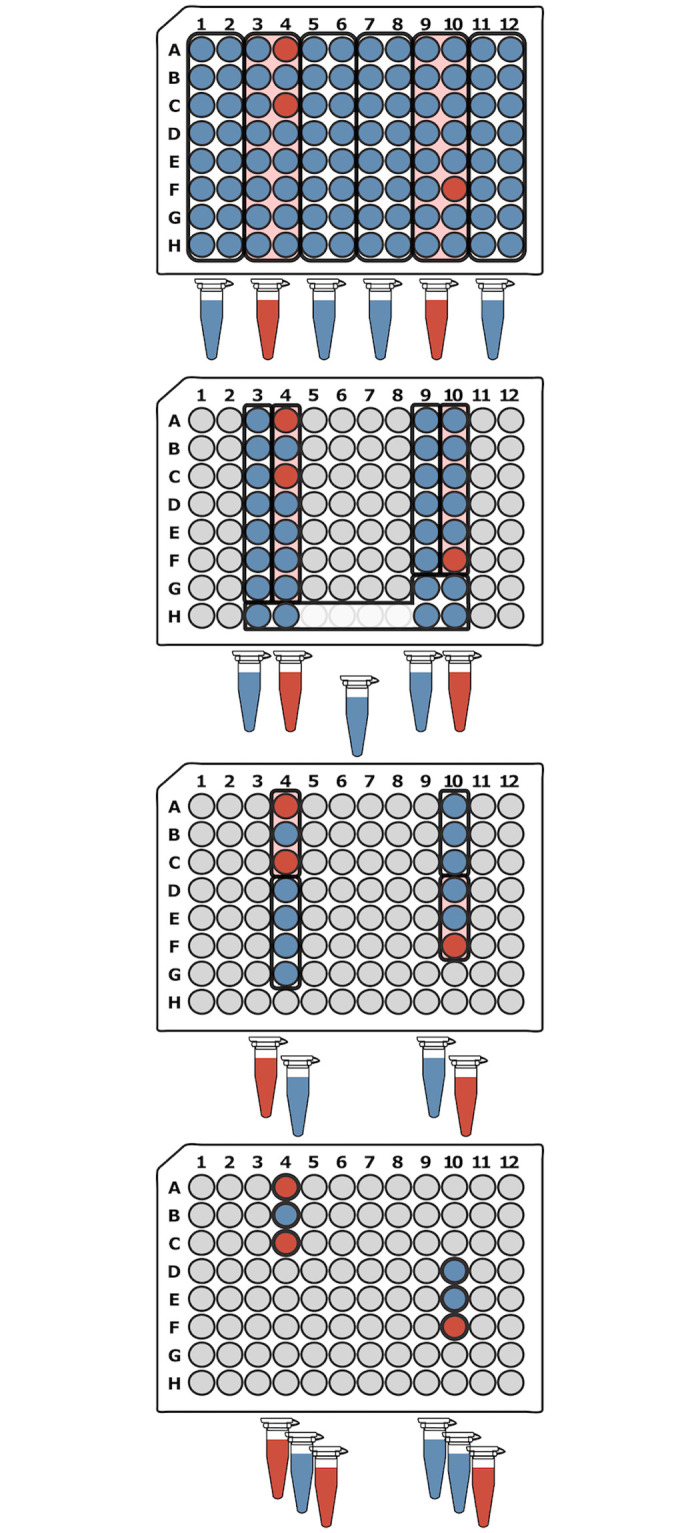
For 96 samples with an estimate of 3 positive samples, the S-Stage algorithm requires 4 steps. In the first step (top 96 well plate), 96 samples are tested in 6 groups (black outline) of 16. In the next step, the samples in the positive pools from the previous step are arbitrarily redivided into 5 groups of 6 or 7 samples and tested. In the third step, the samples from positive pools from step 2 are redivided into 4 groups of 3 or 4. In the final step, individual testing is performed on samples from the positive pools in step 3. The number of tests required depends on the initial arrangement of positive samples within the pools but in this example 21 tests are required to identify 3 positive samples (red wells). The number of tests is lower than the upper bound in this case due to the fortunate placement of two positive samples in the same pool in steps 1-3.
