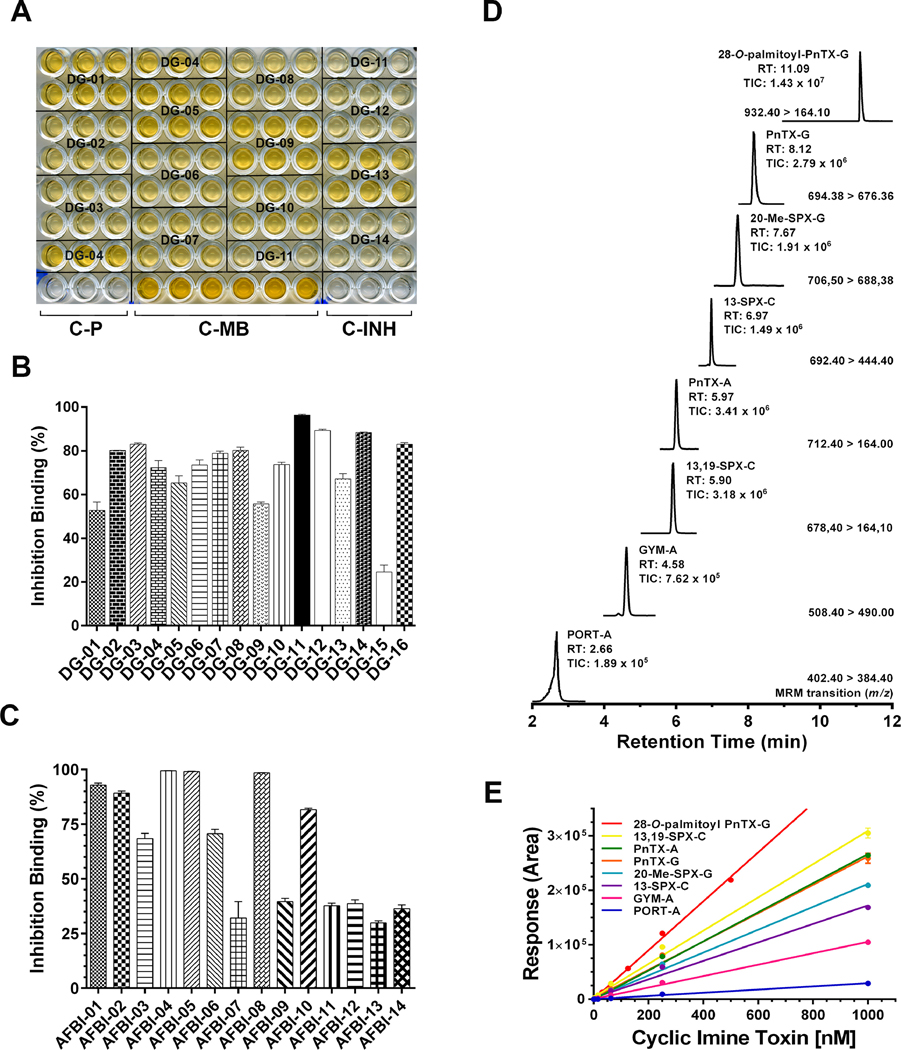
FIGURE 1.
1A. Microplate receptor-binding assay showing the inhibition of biotin-α-bungarotoxin by digestive-gland extracts from mussels collected in Ingril lagoon. DG-samples were analyzed by sextuplicate. Plate signal (C-P): control wells processed without membrane coating. 100% signal (C-MB): control wells in which Torpedo-nAChRs were incubated in the absence of toxin or extract samples. 100% inhibition (C-INH): control wells in which Torpedo-nAChRs were incubated with 1 × 10−6 M α-BgTx. 1B. Inhibition binding potency of digestive-gland extracts from mussels collected in Ingril lagoon. OD492 data were expressed in inhibition percent using Equation 1 (Material and methods). Data are mean values ± SEM of sextuplicate assays of at least two independent experiments. 1C. Inhibition binding potency of shellfish extracts provided by Agri-food and Biosciences Institute (AFBI). OD492 data were expressed in inhibition percent using Equation 1 (Material and methods). Data are mean values ± SEM of sextuplicate assays of at least two independent experiments. 1D. UPLC-MS/MS chromatogram showing the simultaneous analysis of seven cyclic imine toxins and 28-O-palmitoyl ester of pinnatoxin-G. The MRM conditions, retention time and MS-signal are indicated in the figure. 1E. Calibration curves for seven cyclic imine toxins and 28-O-palmitoyl ester of pinnatoxin-G. 5 μl of a toxin standard mix in the concentration range of 1 pM to 1 μM was loaded to the BEH C18 column (see Material and Methods). Toxin quantification was done by integration of the MRM peak area of each analyte.
Abbreviations: DG: digestive glands AFBI: Shellfish samples provided by Agri-food and Biosciences Institute; PORT-A: Portimine-A; GYM-A: gymnodimine-A; 13,19-SPX-C: 13,19-didesmethyl-spirolide-C; PnTX-A: pinnatoxin-A; 13-SPX-C: 13-desmethyl spirolide-C; 20-Me-SPX-G: 20-methyl spirolide-G; PnTX-G: Pinnatoxin-G; Palmitoyl-PnTX-G: 28-O-palmitoyl pinnatoxin-G.