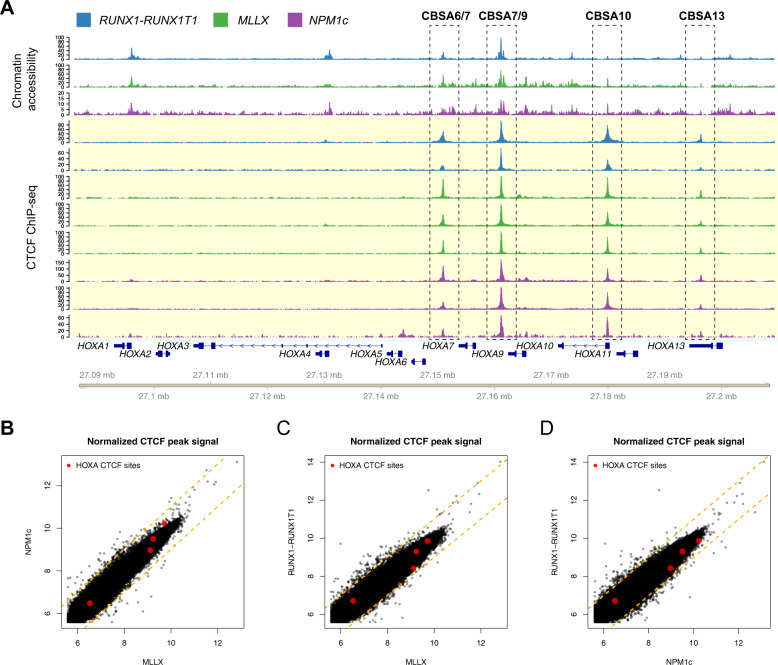
Fig. 1. CTCF is bound to chromatin-accessible sites at the HOXA locus in primary AML samples.
a Chromatin accessibility by ATAC (top tracks highlighted in white; N = 1 from each mutation category, from ref. [1]) and ChIP-seq for CTCF (bottom tracks highlighted in yellow) from primary AML samples with either t(8;21) creating the RUNX1-RUNX1T1 gene fusion (blue; N = 2), MLL rearrangements (green; N = 3), or a normal karyotype and NPM1 mutation (purple; N = 3). CTCF sites CBSA6/7, CBSA7/9, CBSA10, and CBSA13 are indicated by the dashed boxes. b–d Scatter plots comparing the CTCF peak summit counts between each AML type in log2 normalized read counts (mean of three samples for NPM1c and MLL-rearranged samples, mean of two for RUNX1-RUNX1T1). Red points indicate ChIP-seq signal for the four CTCF binding sites highlighted in a, which are similar across AML samples. Dashed orange lines indicate a twofold change between the samples.