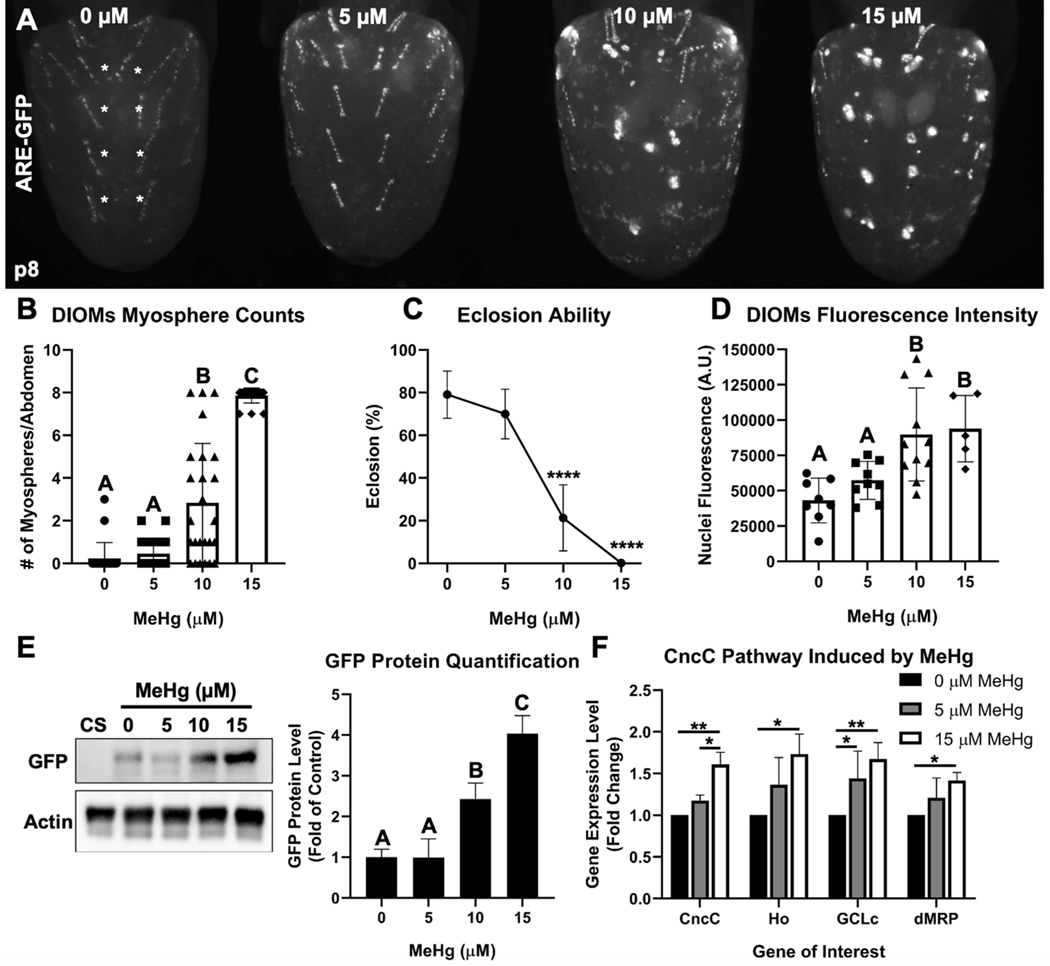
Fig. 3. MeHg induces DIOM myospheres and activates the CncC pathway.
a Representative image of DIOM morphology in ARE-GFP pupa after larval MeHg exposure. b Quantification of myospheres in most medial DIOMs in A2-A5 (denoted by the white asterisks) in ARE-GFP pupa upon larval MeHg exposure (n ≥ 22 abdomens/treatment, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-hoc for multiple comparisons, p<0.05, significant differences indicated by different letter labels). c Eclosion ability of ARE-GFP pupa upon larval MeHg exposure (n = 3, 450 flies/treatment, mean ± s.d.m., Z-test between each treatment group to 0 μM MeHg, ****p<0.0001). d Mean nuclei GFP fluorescence intensity (arbitrary units) of DIOMs upon larval MeHg exposure (100 individual nuclei/abdomen, n ≥ 5 abdomens/treatment). e Representative Western blot of GFP and actin protein bands from whole ARE-GFP pupa protein extracts upon larval MeHg exposure. The Canton S (CS) wild-type strain is a negative control for GFP protein. Quantification of GFP protein band intensities (normalized to actin) is represented as a bar graph (n = 3, d, e mean ± s.d.m., One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD, p<0.05, significant differences indicated by different letter labels). f Gene expression by qPCR of CncC and CncC-regulated genes in Canton S pupa after larval exposure to 0, 5, or 15 μM MeHg (n = 3, mean ± s.d.m., One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD, *p<0.05, **p<0.01).