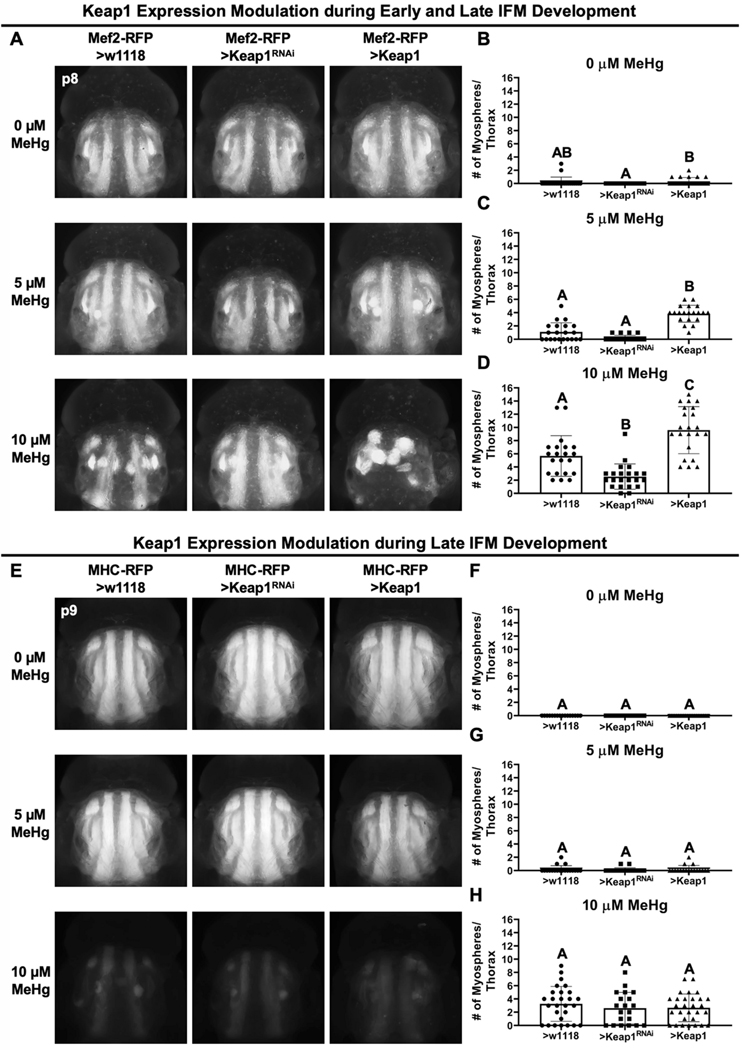
Fig. 6. Muscle-specific CncC signaling modulation of MeHg effects on IFM morphology.
a Representative images of MeHg effects on IFM morphology with either no change (>w1118), knockdown (>Keap1RNAi), or overexpression (>Keap1) of Keap1 with the Mef2-RFP-GAL4 driver. b-d Number of myospheres in each thorax were quantified at indicated MeHg treatment (n ≥ 20/genotype/treatment, mean ± s.d.m., Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-hoc for multiple comparisons, p<0.05, significant differences indicated by different letter labels). e Representative images of IFM morphology with either no change (>w1118), knockdown (>Keap1RNAi), or overexpression (>Keap1) of Keap1 with the MHC-RFP-GAL4 driver. f-h Number of myospheres in each thorax were quantified at indicated MeHg treatment (n ≥ 15/genotype/treatment, mean ± s.d.m., Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-hoc for multiple comparisons, p<0.05, significant differences indicated by different letter labels).