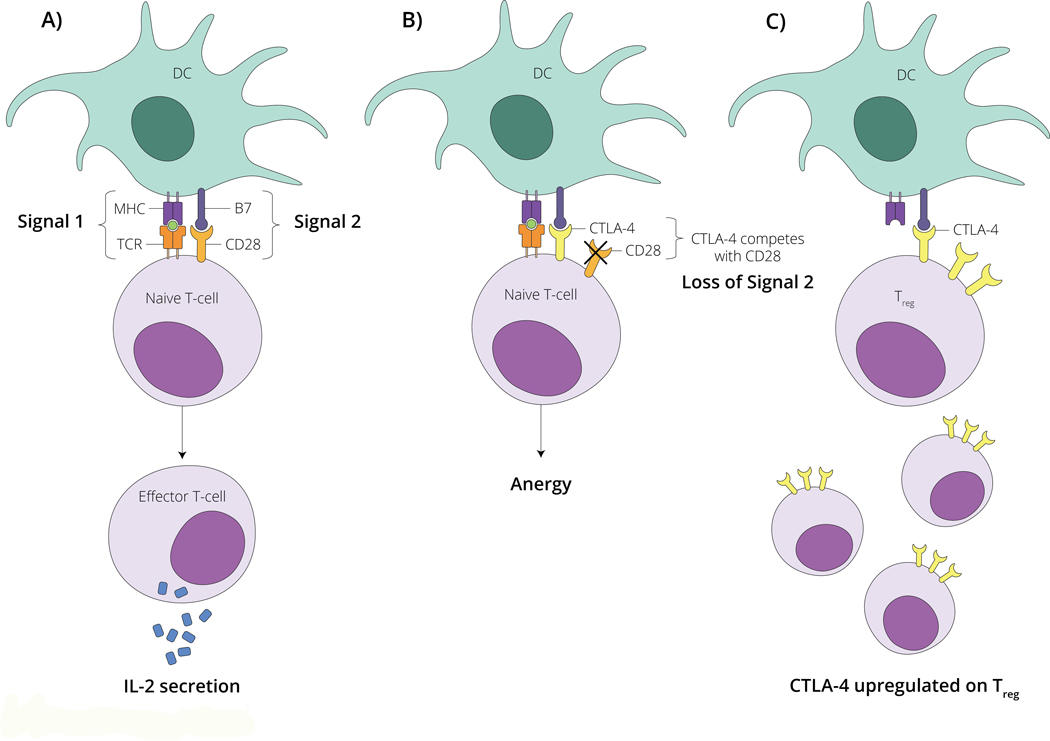
Figure 2 – Schematic overview of CTLA-4 modulated T cell function.
A) T cell are activated by dendritic cells (DC) via signal 1 (MHC-antigen-TCR binding) and signal 2 (B7-CD28 binding) leading to a naïve t cell becoming a functional effector T cell capable of secreting interleukin-2 (IL-2) which serves to further propagate the immune response. B) CTLA-4 on the surface of T cells competes with CD28 for B7 binding. When CTLA-4 binds to B7 (loss of signal 2), a signaling cascade is induced that leads to T cell anergy. C) CTLA-4 is upregulated on the surface of regulatory T cells (Treg). This leads to a predominance of B7-CTLA-4 binding among this T cell subset. Modulating CTLA-4 with therapeutic antibodies can lead to effective anti-tumor immune responses. Please see accompanying text for further details.