Figure 1: An ERK-KTR targeted mouse line for live visualization of ERK activity in vivo.
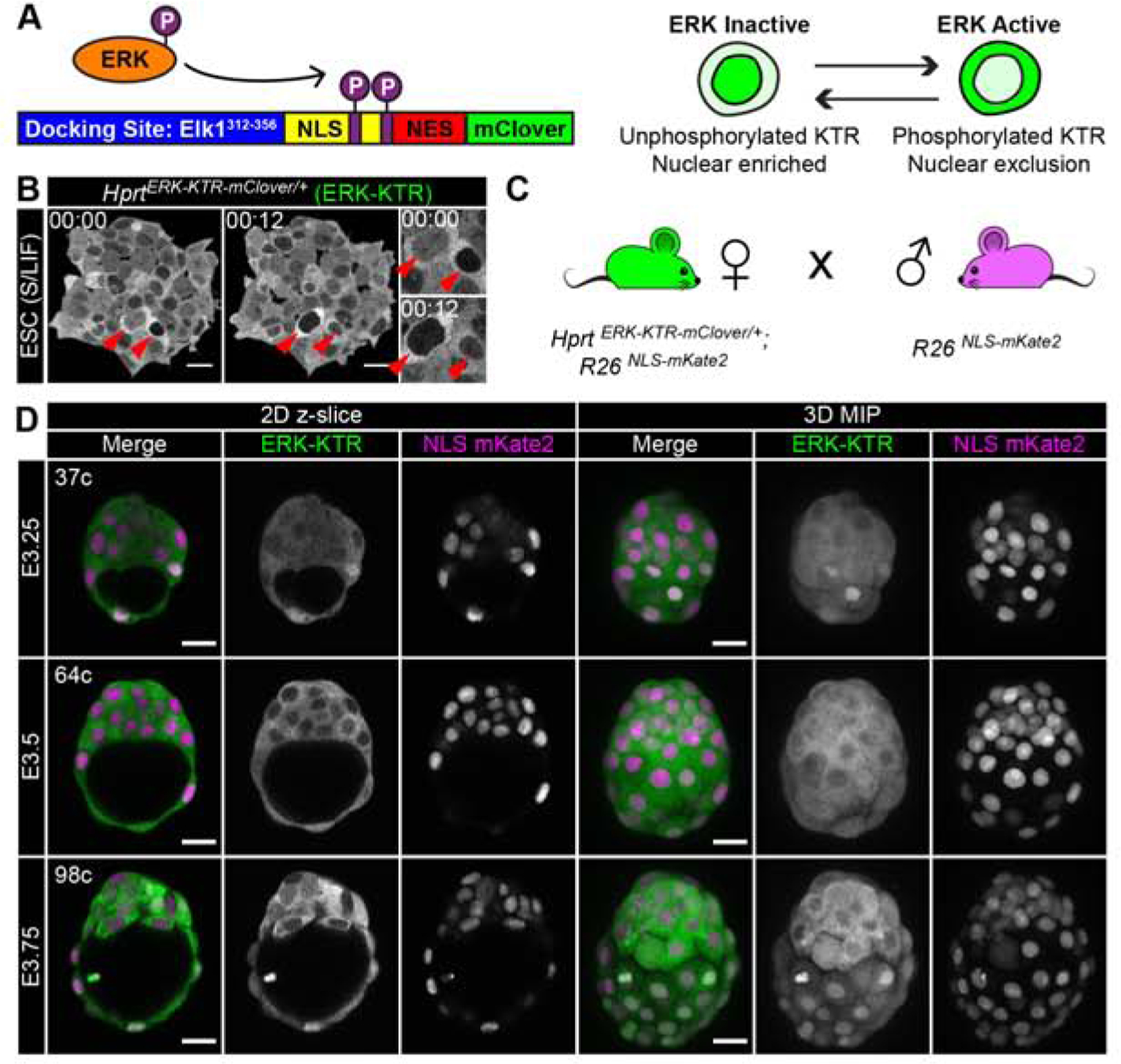
(A) Schematic of ERK kinase translocation reporter (ERK-KTR). ERK-KTR is a biosensor, which shuttles between cytoplasm and nucleus as a read-out of ERK kinase activity. NLS: nuclear localization signal. NES: nuclear export signal. P: Phosphorylation. (B) Time-lapse confocal images of mouse embryonic stem cells (ESC) expressing HprtCAG-ERK-KTR-mClover, abbreviated to HprtERK-KTR. Red arrows indicate two cells at different times. Inset shows higher magnification. Timestamp shows Hour:Min. S/LIF: Serum LIF culture conditions. (C) Summary diagram of mouse cross used to generate hemizygous HprtERK-KTR and homozygous R26NLS-mKate2 embryos in this study. (D) Confocal images of hemizygous HprtERK-KTR and homozygous R26NLS-mKate2 embryos during pre-implantation development. Embryonic day (E) and cell number are indicated for staging. Scale bars: 20μm.
