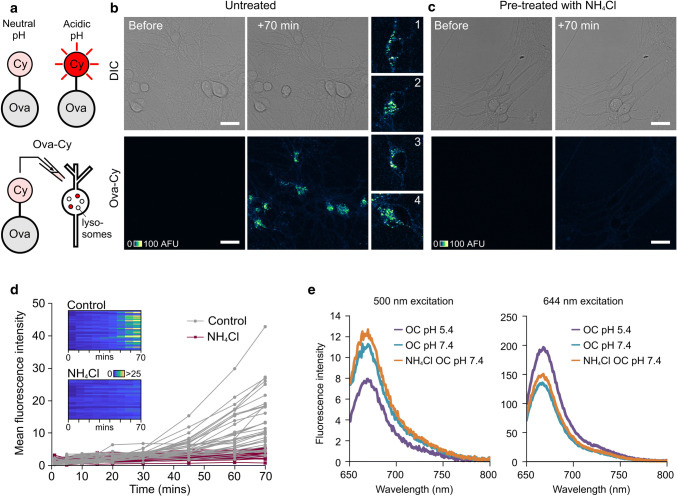
Fig. 4.
Protein-conjugated CypHer5E reports its pH environment. a CypHer5E conjugated to ovalbumin fluoresces upon uptake into intracellular acidic compartments. b Confocal images showing increase in fluorescence 70 min after addition of Ova-Cy to primary hippocampal neurons. c No fluorescence increase is observed in cells pre-treated with NH4Cl, a weak base that raises the pH of acidic compartments. One 1.0-μm slice is shown. Scale bar is 25 μm. d Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity from cells shown in b and c. Each trace represents an individual cell body either untreated (grey, n = 34) or pre-treated with 10 mM NH4Cl for 30 min (purple, n = 28). Data pooled from three independent experiments, 3–4 FOV per experiment. Colour bar for look-up table indicates mean fluorescence intensity. e Fluorescence arising from Ova-Cy diluted into buffer of pH 5.4 (purple) or 7.4 (turquoise). Ova-Cy diluted into buffer containing NH4Cl, pH 7.4 is also shown (orange). The absorbance maximum for CypHer5E at physiological pH 7.4 is 500 nm (left plot) and at pH 5.4 (similar to the pH in a lysosome) is approximately 645 nm. Ova-Cy in acidic (pH 5.4) buffer has increased intensity over neutral pH when excited with 644 nm light. The presence of NH4Cl has no effect on the spectral properties of the dye