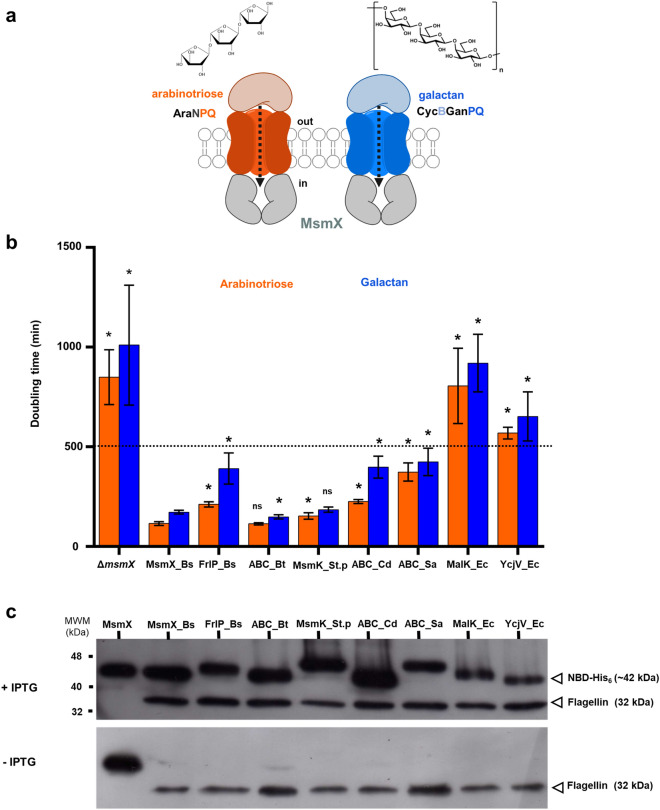
Figure 2.
Functionality of MsmX homologs tested by their ability to support growth in distinct oligosaccharides. (a) Schematic representation of the AraNPQ and GanSPQ(CycBGanPQ) transport systems of B. subtilis, which import arabino- oligomers (orange) and galacto-oligomers (blue), respectively. (b) Growth kinetics parameters of the msmX-null mutant B. subtilis strain (IQB495) and the strains carrying different NBD alleles, ISN10(msmX_Bs), ISN15(frlP_Bs), ISN11(ABC_Bt), ISN12(msmK_St.p), ISN25(ABC_Cd), ISN13(ABC_Sa), ISN14(malK_Ec), ISN17(ycjV_Ec), were determined in the presence of arabinotriose (orange) or galactan (blue). The doubling time of each strain in the presence of the inducer IPTG is shown. A value above 500 min (dashed line) is considered no growth (see Supplementary Table 1). At least three independent experiments were performed in each condition and error bars indicate the standard deviation of the mean. Statistical significance between doubling time of each strain bearing a MsmX homolog and the strain ISN10 (msmX_Bs) is indicated (*p < 0.05; ns: not significant) and was obtained using the R software version 3.6.2 (https://www.r-project.org/). (c) Western blot analysis of NBD accumulation in total cell extracts of each strain grown in the presence (top panel) or absence (bottom panel) of IPTG. Purified MsmX-His6 (0.25 μg) was loaded on the first lane. Low Molecular Weight, Protein Marker II (NZYTech) was used and is partially represented (MWM). NBDs and flagellin (loading control) detection are indicated by open arrowheads. Uncropped images of these blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 5.