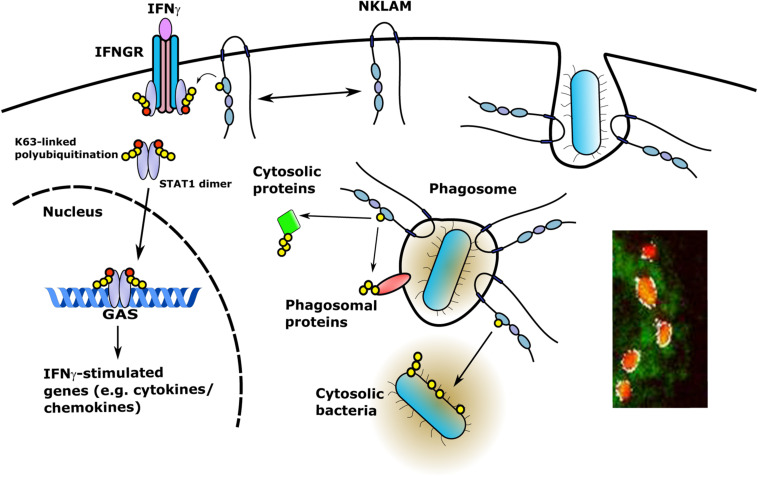
FIGURE 4.
NKLAM in macrophage immune function. Upon exposure to IFNγ, STAT1 is phosphorylated and NKLAM is transiently associated with the IFNγ-IFNGR complex at the plasma membrane. In this location, NKLAM is in close proximity to STAT1, which would allow NKLAM to ubiquitinate STAT1 or other proteins to promote STAT1 transcriptional activity. After ingestion of bacterial targets, NKLAM is localized to the phagosome membrane with the catalytic RING2 domain and C-terminal tail facing the cytoplasm. This would provide NKLAM with access to phagosome membrane proteins and cytosolic target proteins, as well as bacteria that escape the phagosome. Red circles; phosphotyrosine, yellow circles; ubiquitin. Immunomicrograph insert: Macrophage phagosomes after ingestion of fluorescent-labeled E. coli (red). NKLAM staining: green; Image J-defined co-localization of E. coli and NKLAM: white. Adapted from Lawrence, D.W., and Kornbluth, J. E3 ubiquitin ligase NKLAM is a macrophage phagosome protein and plays a role in bacterial killing. Copyright 2012, with permission from Elsevier and Lawrence D.W., and Kornbluth, J. E3 ubiquitin ligase NKLAM ubiquitinates STAT1 and positively regulates STAT1-mediated transcriptional activity. Copyright 2016, with permission from Elsevier.