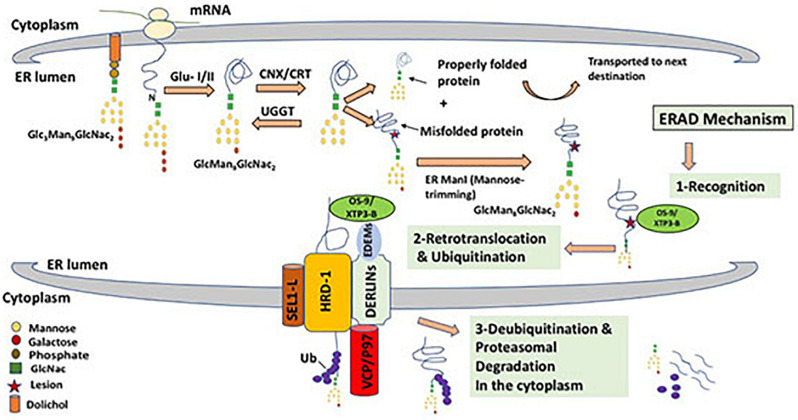
FIGURE 2.
ERAD mechanism for misfolded glycoprotein through the HRD-1/SEL-1L complex. Triglycosylated form of protein-bound oligosaccharide (Gl3Man9GlcNac2) is processed by glucosidase enzymes (GluI/II) that cleaves off two glucose molecules. This is followed by cycles of interaction between the nascent protein and lectins such as Calnexin and Calreticulin (CNX/CRT), that binds specifically to monoglucosylated oligosaccharides (GlMan9GlcNac2) and ensure the proper folding of newly synthesized protein. This cycling effect is generated by the enzyme UDP-glucose:glycoprotein glucosyltransferase (UGGT), that transfers back a glucose residue to the improperly folded protein to enable further encounters with the ER chaperones (CNX/CRT). A properly folded protein is then released after the cleavage of the remaining glucose molecule. Properly formed protein is dispatched to its functional destination, while misfolded protein that cannot reach its mature form will undergo mannose cleavage by ER α1,2-mannosidase I (ERMan1), which produces Man8GlcNAc2. Terminal mannose cleavage (α mannose) function as a recognition signal for ERAD lectins OS-9 and XTP3-B that recognize and binds to exposed mannose residues after cleavage of α mannose. The three chaperones EDEM1, OS9 and XTP3-B function together as recognition complex that interacts with misfolded proteins and the HRD-1/SEL-1L retrotranslocation channel. Derlins which are candidates for the translocon channel also interacts with the EDEMs and facilitates the interaction of EDEMs with cytosolic AAA-ATPase p97, that provides ATP hydrolysis for successful extraction of mutant proteins. Retrotranslocation is coupled by Uniquitination, a process that targets proteins for degradation by 26S proteasome by tagging them with ubiquitin chains.