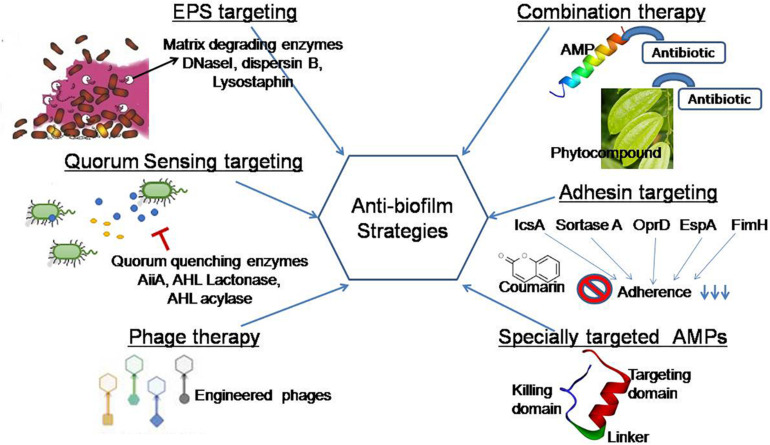
FIGURE 4.
Graphical representation of anti-biofilm strategies covered in this review. EPS targeting: EPS matrix is targeted by matrix-degrading enzymes (DNaseI, dispersin B, lysostaphin) that inhibit microbial adhesion to a surface. Quorum sensing targeting: This strategy focused on the use of natural agents that block cell–cell communication in preformed biofilms and regulate virulence factor production (Shastry et al., 2019). Phage therapy: Engineered phages degrade the matrix exopolysaccharide by producing polysaccharide depolymerase enzymes. Specially targeted AMPs: This novel strategy targets in a species-specific manner due to the presence of species targeting peptides (Xu et al., 2020). Adhesin targeting: Phytocompounds target adhesin proteins and blocked biofilm formation at the beginning (Adnan et al., 2020). Combination therapy: Natural anti-biofilm agents function effectively in a combined approach in comparison with its single use.