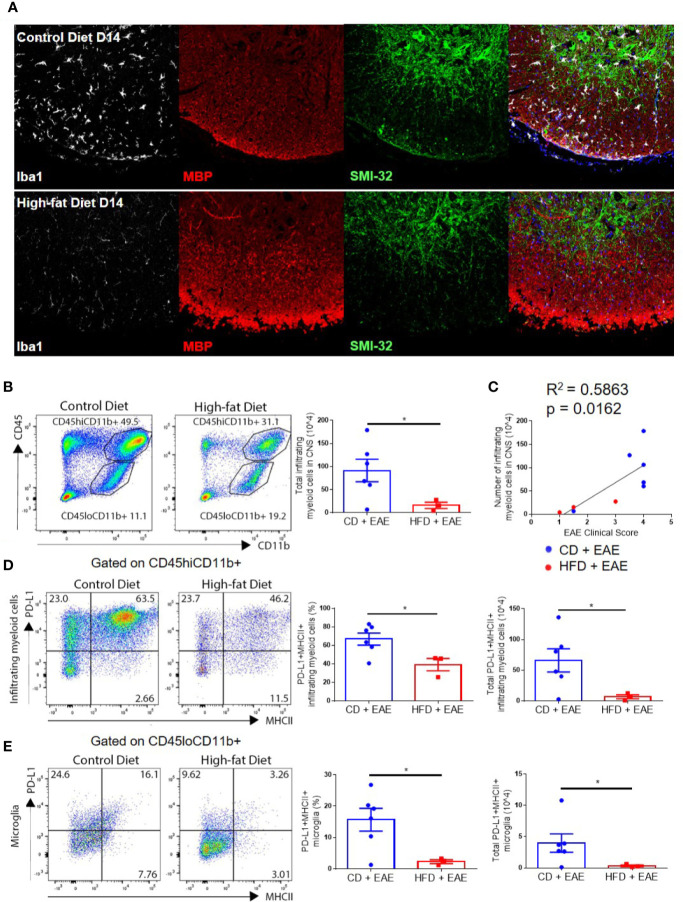
Figure 3.
Numbers of infiltrating myeloid cells and PD-L1 upregulation correlate with EAE disease severity. (A–E) C57BL/6 male mice were placed on CD or HFD for 6–7 months induced with EAE. (A) Iba1 (white), myelin basic protein (red), and SMI-32 (green) immunoreactivity in spinal cords isolated from CD or DIO mice on day 14 post-immunization. (B) Representative flow plots and gating strategy for infiltrating myeloid cells (CD45hiCD11b+) and microglial cells (CD45loCD11b+) in the CNS on day 16 post-immunization. Total numbers of infiltrating myeloid cells in the CNS on day 16 post-immunization. (C) Numbers of infiltrating myeloid cells (CD45hiCD11b+) cells in CNS vs. EAE clinical score on day 16 post-immunization. (D) Representative flow plots indicating expression of PD-L1 and MHCII on infiltrating myeloid cells (left panels), percentage of PD-L1+MHCII+ infiltrating myeloid cells (middle panels), and total number of PD-L1+MHCII+ infiltrating myeloid cells (right panels) in the CNS on day 16 p.i. (E) Representative flow plots indicating expression of PD-L1 and MHCII on microglia (left panels), percentage of PD-L1+MHCII+ microglia (middle panels), and total number of PD-L1+MHCII+ microglia (right panels) in the CNS on day 16 p.i. Sample size n = 3–6/group; combined from two different experiments. Bar graphs depict mean ± SEM. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test used to compare two groups. *p < 0.05.