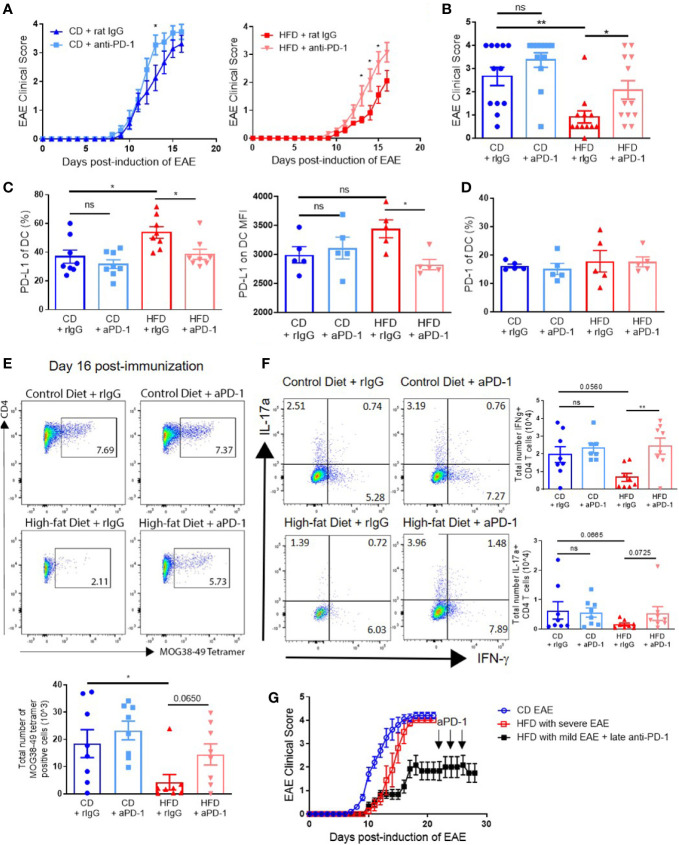
Figure 6.
PD-1 blockade during priming restores EAE clinical course in DIO mice. (A-G) C57BL/6 male mice were placed on CD or HFD for 6-7 months and immunized subcutaneously with 300 μg (A-F) or 100 μg (G) MOG35-55 peptide in 5 mg/ml HKMT CFA and 200ng pertussis toxin on day 0 and 2 p.i. For PD-1 blockade, the treatment schedule was 500 μg on day 0 and 250 μg on days 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 p.i. (A-F), or 500 μg on day 22 and 250 μg on days 24 and 26 p.i. (G). (A) EAE clinical score of CD and DIO mice treated with anti-PD-1 or control rat IgG. (B) EAE clinical score on day 14 p.i. from A. (C) Percentages of DCs expressing PD-L1 and MFI of PD-L1 on DCs in spleen on day 16 p.i. (D) Percentages of DCs expressing PD-1 in spleen on day 16 p.i. (E) Representative flow plots and numbers of MOG38-49 tetramer staining of CD4+ T cells in CNS on day 16 p.i. (F) Representative flow plots and numbers of CD4+ T cells expressing IFN-γ and IL-17α in the CNS on day 16 p.i. (G) EAE clinical score of DIO mice that did not initially develop clinical disease treated with anti–PD-1 during chronic phase. EAE clinical scores and bar graphs depict means ± SEM. (A-E) Sample size n = 8/group and is combined from two different experiments. (G) Sample size n = 4–10/group and is representative of three different experiments. Significance for differences in clinical scores was determined by Mann-Whitney ranking U test. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey test. Two-tailed unpaired Student t-test used to compare two groups for cell count data when needed. ns: not significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.