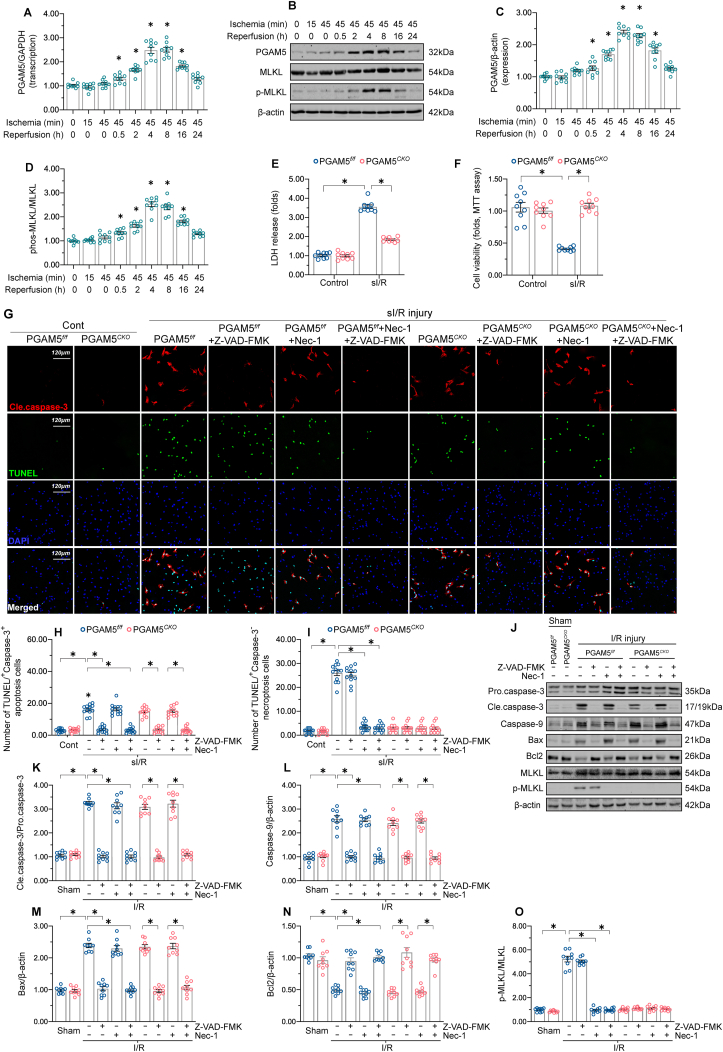
Fig. 1.
PGAM5 upregulation promotes cardiomyocyte necroptosis after I/R injury. (A) Evaluation of cardiac PGAM5 expression through qPCR in mice subjected to I/R surgery. (B) Western blot detection of cardiac PGAM5 and phospho-MLKL expression following I/R injury. (C–D) Quantitative analysis of PGAM5 and phospho-MLKL levels in heart samples processed for western blotting. (E) Evaluation of cardiomyocyte necrosis through the LDH release assay. (F) MTT assay was used to evaluate cell death. (G–I) Representative images of TUNEL and caspase-3 double immunofuorescence in PGAM5f/f and PGAM5CKO cardiomyocytes. The apoptosis inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK and the necroptosis blocker Necrostatin-1 were applied to isolated cardiomyocytes before sI/R injury. (J–O) Western blot detection of apoptosis- and necroptosis-related proteins in heart extracts from PGAM5f/f and PGAM5CKO mice subjected to I/R injury. Before I/R injury, the mice were injected with the apoptosis inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK or the necroptosis blocker Necrostatin-1. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results. Data are shown as the means ± SEM, n = 6 mice or 3 independent cell isolations per group. *p < 0.05.