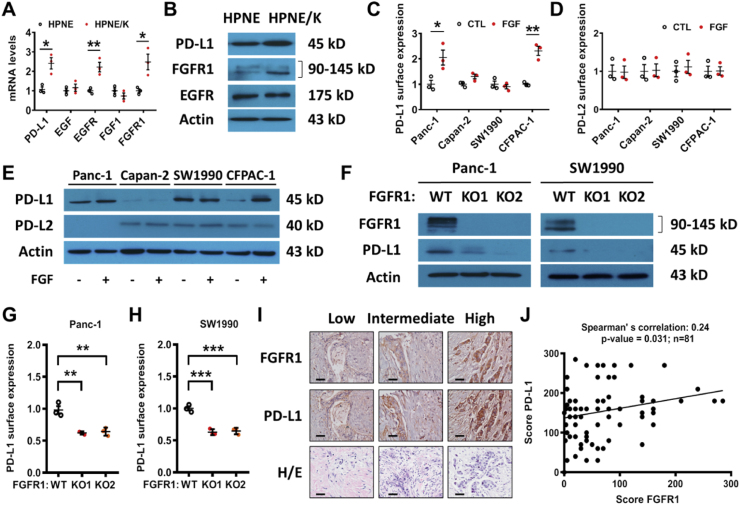
Fig. 4.
Effect of inhibition of EGFR and FGFR on PD-L1 expression in cancer cells. (A) Impact of K-ras on expression of PD-L1, EGF, EGFR, FGF1 and FGFR1 mRNA in HPNE cells, measured by qRT-PCR analysis. (B) Expression of PD-L1, FGFR1, and EGFR in HPNE cells stably transfected with K-ras (HPNE/K) in comparison with their parental HPNE cells. Protein levels were measured by immunoblotting analysis. Data are representative of three separate experiments. (C–D) Four human pancreatic cell lines were incubated with FGF1 and FGF2 (50 ng/ml). Cell surface PD-L1 and PD-L2 expressions were quantified by FACS analysis. (E) Four human pancreatic cell lines were incubated with FGF1 and FGF2 (50 ng/ml). Expressions of PD-L1 and PD-L2 were measured by immunoblotting. (F) Expressions of PD-L1 and FGFR1, in Panc-1 and SW1990 FGFR1 KO cells, were measured by immunoblotting. (G-H) PD-L1 cell surface expression in Panc-1 and SW1990 FGFR1 KO cells was quantified by FACS analysis. (I-J) Correlation between PD-L1 and FGFR1 expression in human pancreatic tumor samples (n=81) using tissue microarray. The protein expression was determined by immunohistochemistry staining. Representative images of immunostaining and H/E staining (scale bars, 50 μm) are shown in (I); the quantitative data are shown in (J). Data are means ± SEM of three separate experiments; Two-tailed unpaired t-test for A, C-D; One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test for G-H. Spearman’s rank correlation test for J. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.