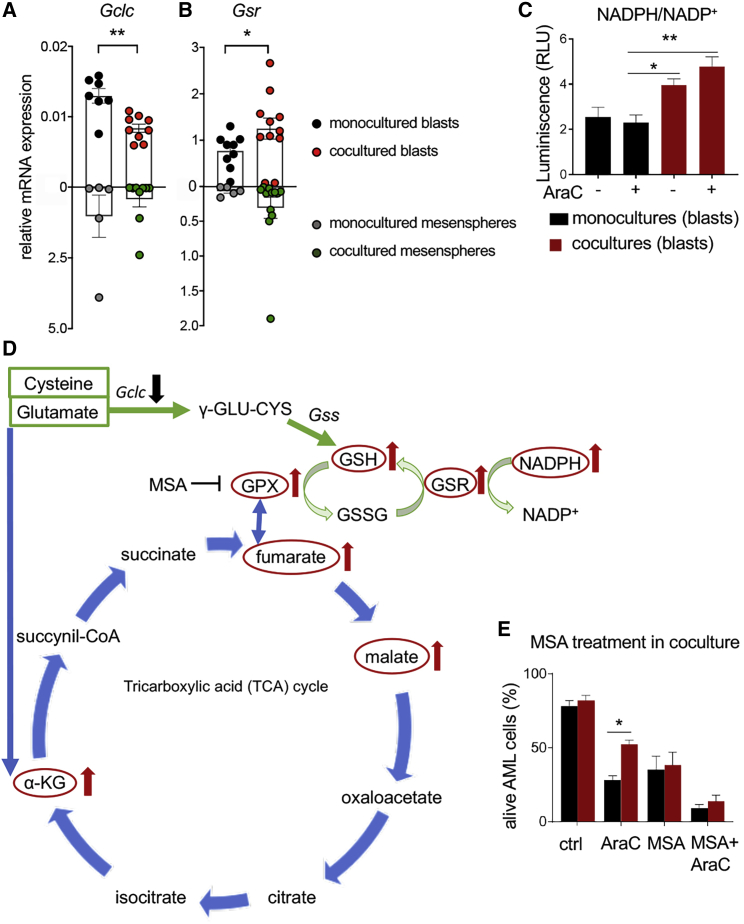
Figure 6.
BMSCs Protect Leukemic Blasts from Chemotherapy through GSH Recycling and Oxidation by Gpx
(A and B) mRNA expression of the genes encoding (A) the catalytic subunit of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase (Gclc), which is the first rate-limiting enzyme of GSH synthesis, and (B) GSH reductase (Gsr), required for GSH recycling in AML blasts and BMSCs, cultured alone (black, blasts; gray, BMSCs) or together (red, blasts; green, BMSCs) for 24 h in presence of AraC. Each dot is a biological replicate.
(C) NADPH/NADP+ ratio in sorted CD45+ leukemic blasts after monoculture (black) or coculture with BMSCs (red), in the presence/absence of AraC (n = 3).
(D) Schematic representation of the TCA cycle and glutathione redox cycle, indicating with arrows upregulated (red) and downregulated (black) molecules in coculture.
(E) Frequency of alive (AnnexinV−DAPI−) AML cells 24 h after treatment of monoculture (black) or cocultured (red) cells with vehicle (ctrl), AraC, the Gpx inhibitor mercaptosuccinic acid (MSA, 1.6 mM) or both drugs (n = 6).
(B–E) Data represent mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. (B and C) Unpaired 2-tailed t test. (D–F) One-way ANOVA followed by pairwise Bonferroni comparisons.