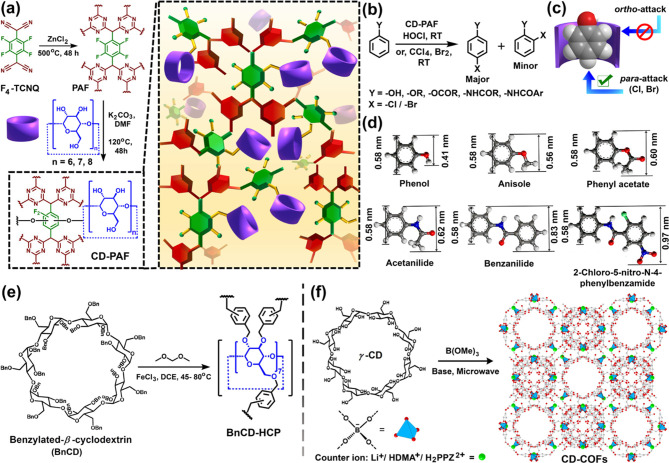
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic representation for the synthesis of the porous aromatic framework (PAF) based on tetrafluorotetracyanoquinodimethane (F4-TCNQ) by an ionothermal process and the postmodification of the resultant PAF through SNAr reaction with α-, β-, and γ-cyclodextrins, leading to the formation α-CD-PAF, β-CD-PAF, and γ-CD-PAF, respectively, exhibiting high catalytic activity toward regioselective p-halogenation of substituted aryl compounds. (b) Reaction scheme of halogenation of diverse aryl compounds catalyzed by CD-PAFs. (c) Pictorial representation of the inclusion complex of phenol and cyclodextrin (only para-position of phenols is accessible for electrophilic substitution upon inclusion to CD-PAF). (d) Molecular dimensions of various aromatic substrates (phenol, anisole, phenylacetate, acetanilide, benzanilide, and 2-chloro-5-nitro-N-phenyl benzamide), % of selective p-halogenation decreases with increasing substrate size. (e) Schematic representation of β-CD-based hyper-cross-linked polymer (BnCD-HCP) obtained through Friedel–Crafts alkylation using dimethoxy methane as an external cross-linkers; Au nanoparticles-doped BnCD-HCP exhibited high catalytic activity for nitrophenol reduction. (f) Condensation of γ-CD with trimethyl borate(B(OMe)3) in the presence of lithium hydroxide (LiOH), dimethylamine (DMA), or piperazine (PPZ) under microwave conditions to afford crystalline γ-CD-covalent organic frameworks (CD-COFs) with different counterions. CD-COFs were employed for selective CO2 adsorption and Li+ ion storage. Panels d and f were adapted with permission from ref (7g) (copyright 2017 American Chemical Society) and ref (7d) (copyright 2017 John Wiley and Sons).