Figure 5.
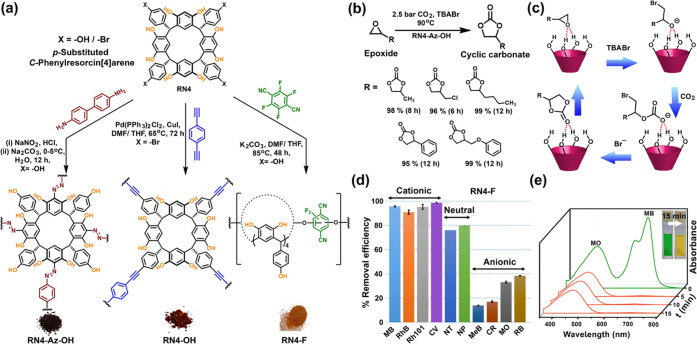
(a) Schematic illustration for the synthesis of C-phenylresorcin[4]arene (RN4)-based porous organic polymers: RN4-Az-OH, RN4-OH, and RN4-F through the diazo coupling, Sonogashira cross-coupling, and aromatic nucleophilic substitution reaction, respectively. (b) Conversion of epoxide and CO2 to cyclic organic carbonates using RN4-Az-OH as a catalyst. (c) Plausible mechanism of the catalytic CO2 fixation. (d) Size-selective, charge-specific organic dye removal from water by RN4-F polymer (MB, methylene blue; RhB, rhodamine B; Rh101, rhodamine 101; CV, cresyl violet; NT, β-naphthol; NP, 4-nitrophenol; MeB, methyl blue; CR, Congo red; MO, methyl orange; RB, Rose Bengal). (e) Separation of cationic methylene blue from anionic methyl orange. Panels d and e were adapted from ref (7k). Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society.