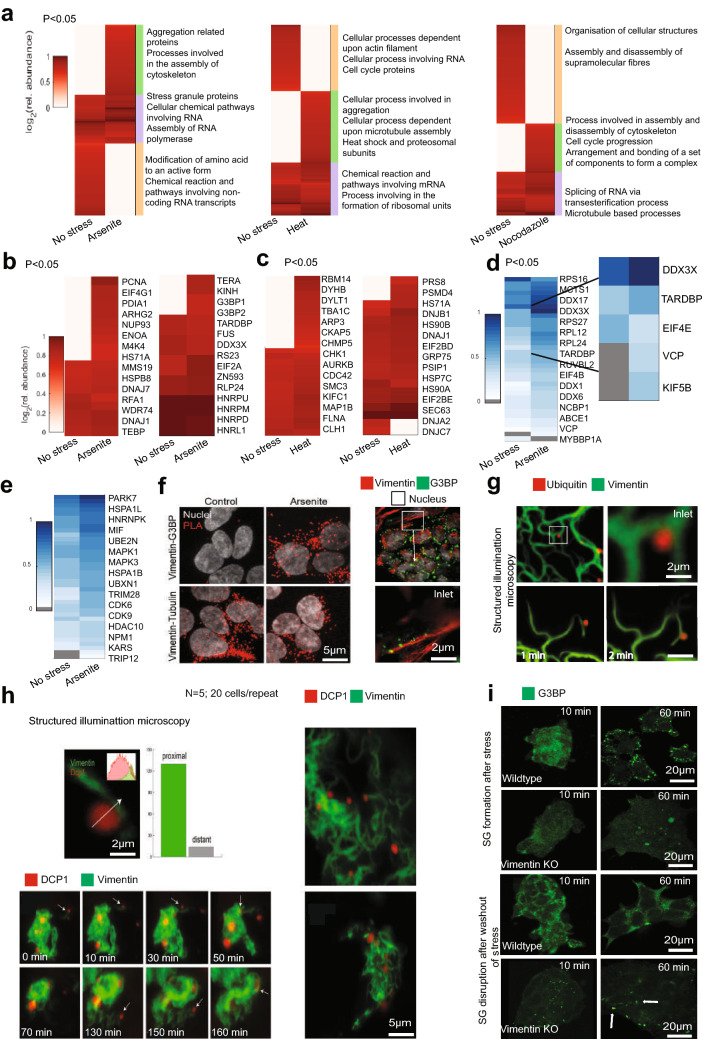
Figure 3.
BioID of Vimentin Interactome identifies protein folding quality control components, RNA-binding proteins, and Stress Granule proteins. (a) Vimentin interactome in (1) No stress (2) Arsenite stress (150 μM/2 h), (3) Heat stress (44 °C/2 h) and (4) Nocodazole. GO analysis and heat maps relative to No Stress condition. (b) Vimentin interacts with stress response proteins (Left panel) and RNA-binding and Stress Granule proteins (Right panel) during Arsenite stress. (c) Vimentin interacts with proteins involved in microtubule based processes (Left panel) and heat shock, proteasomal subunits and other stress related proteins (Right panel) during heat stress. (d) Immunoprecipitation for Vimentin. Heat Map for RBPs binding with Vimentin. (e) Immunoprecipitation for Vimentin. Heat Map for stress regulating proteins binding to Vimentin. (a–e: Heat maps were plotted using established protocols in Matlab (Matlab 2019a Mathworks Ltd). https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab.html?s_tid=hp_products_matlab. (f) Proximity ligation assay was performed on 4 day retinoic acid (1 μg/ml) differentiated mESCs between Vimentin—G3BP (Top panel) and Vimentin—Tubulin (positive control) (Bottom panel). PLA signal was observed between vimentin and G3BP only during arsenite stress. PLA signal was observed between vimentin and tubulin with and without arsenite stress (150 μM/2 h). (Right Panel) Confocal images of differentiated mESCs stained for G3BP (green), Vimentin (red) and Nucleus (white) during arsenite stress. The inlet image shows G3BP aggregates (green) attaching to vimentin filament (red). (g) Structured Illumination Microscopy images of Vimentin-GFP (green) binding to RFP ubiquitin- positive foci (red) in live cells. The interaction of Vimentin and ubiquitin persists over time shown by the time-lapse. (h) Vimentin-GFP (green) interacting with DCP1-RFP (a P-body component and RNA-binding protein) over time and the graph showing the association between the two. The experiment was repeated 5 times. 20 cells were selected to be imaged during each repeat. (i) Confocal images of Wildtype and Vimentin Knockouts differentiated with retinoic acid (1 μg/ml) fixed and stained with G3BP (green). Top panels—Stress induced with arsenite (150 μM) before fixing. Bottom Panels—Stress induced with arsenite (150 μM/1 h) and new media added to cells. The cells were fixed at 10 min and 60 min. The G3BP aggregates were observed to be dissociated after 60 min in the Wildtype cells, whereas the aggregates persisted in the Vimentin Knockout cells. f–i Images were acquired and processed using NIS elements software (version 3.2).