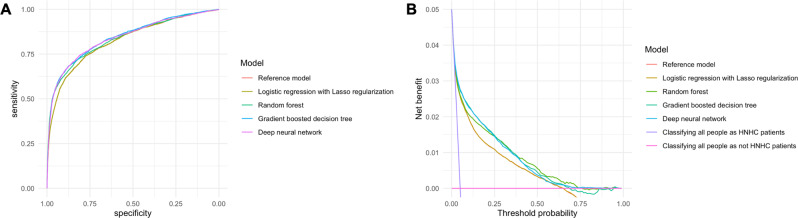
Fig. 2. Prediction ability of the reference and machine-learning-based prediction models for HNHC patients.
A Receiver-operating-characteristics (ROC) curves. The corresponding values of the area under the receiver-operating-characteristics curve for each model (i.e., the c-statistics) are presented in Table 2. B Decision curve analysis. The X-axis indicates the threshold probability for HNHC patients. The Y-axis indicates the net benefit. The curves (decision curves) indicate the net benefit of models (the reference model and four machine-learning-based models) as well as two clinical alternatives (classifying no people as HNHC patients vs. classifying all people as HNHC patients) over a specified range of threshold probabilities of outcome. Compared to the reference model, the net benefit, which is defined as the following equation, for all machine-learning-based models was greater across the range of threshold probabilities. “net benefit = (1 − false negative) × prevalence − false positive × (1 − prevalence) × the odds at the threshold probability”. HNHC patients = high-need, high-cost patients.