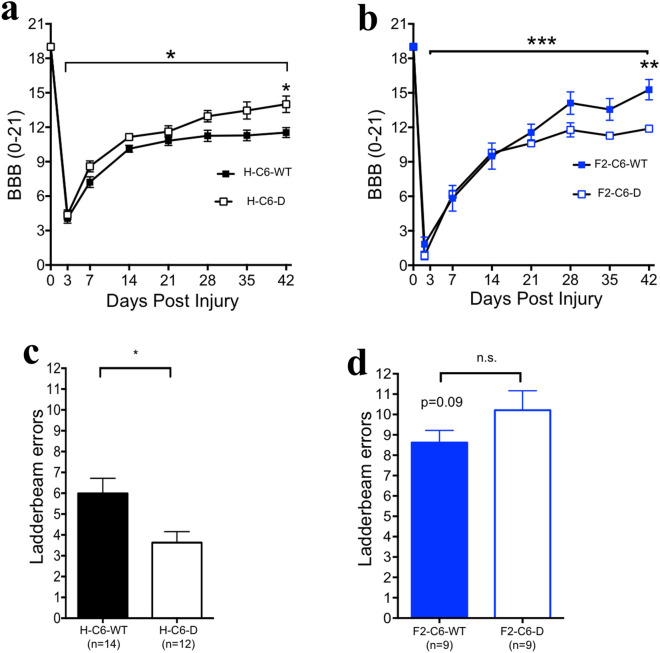
Figure 3.
F2-C6-D PVG rats demonstrated reduced locomotor recovery compared to F2-C6 WT PVG rats. (a) Comparison of BBB scores showed that H-C6-deficient rats exhibited improved functional recovery throughout the duration of the study compared to H-C6 WT PVG rats (two way repeated measures ANOVA, *p < 0.05). Post hoc tests revealed a significant group difference 42 days post injury (Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons, *p < 0.05). (b) Comparison of BBB scores showed that F2-C6-deficient rats exhibited impaired functional recovery throughout the duration of the study compared to F2-C6 WT PVG rats (two way repeated measures ANOVA, *p = 0.0006). Post hoc tests revealed a significant group difference 42 days post injury (Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons post-hoc at day 42, **p < 0.01). (c) Terminal behavioral assessment (42 days post injury) on the horizontal ladderbeam task demonstrated that H-C6-D rats made significantly fewer errors compared to H-C6 WT (Student’s t test, #p < 0.05). (d) When comparing F2-C6-D rats performed no different from F2-C6 WT in ladderbeam errors. However there was a strong trend for F2-C6-D rats having more errors (Student’s t test, p = 0.09). Data points represent group means ± SEM.