Figure 5.
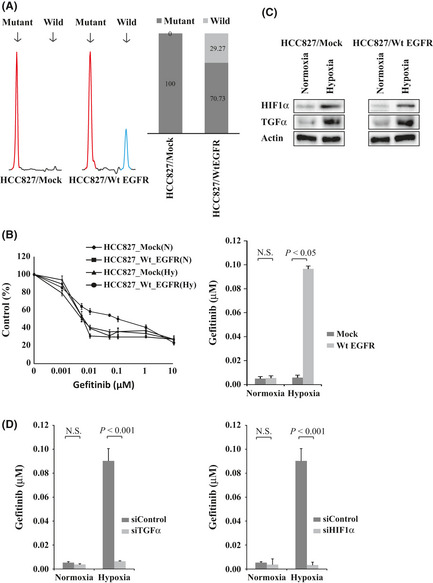
Transfection of wild‐type epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene into HCC827 cells harboring the activating EGFR mutation. (A) Transfectants of the empty vector and wild‐type EGFR were designated HCC827/Mock and HCC827/Wt EGFR cells, respectively. Left: Electropherograms of the fragment analysis for the HCC827/Mock and HCC827/Wt EGFR cells. Red peak, amplified PCR fragment of exon 19 deletion mutation EGFR; blue peak, wild‐type EGFR. Right: Relative proportions of mutant and wild‐type EGFR expression by fragment analysis. Black bar, mutant EGFR; gray bar, wild‐type EGFR. (B) HCC827/Mock and HCC827/Wt EGFR cells were incubated under hypoxia or normoxia for 48 h followed by treatment with gefitinib. The IC 50 value of the HCC827/Wt EGFR cells was significantly higher than that of the HCC827/Mock cells under hypoxia. P = 0.014. (C) HIF1α and TGFα expression was upregulated by hypoxia in the HCC827/Mock cells (left) and the HCC827/Wt EGFR cells (right) as indicated by Western blotting. (D) HCC827/Wt EGFR cells were transfected with siTGFα or siControl (left) or with siHIF1α or siControl (right) then incubated under hypoxia or normoxia for 48 h, followed by treatment with gefitinib. The IC 50 values of the HCC827/Wt EGFR cells were significantly reduced by the knockdown of TGFα or HIF1α under hypoxia (P < 0.001, P < 0.001, respectively).
