Figure 4.
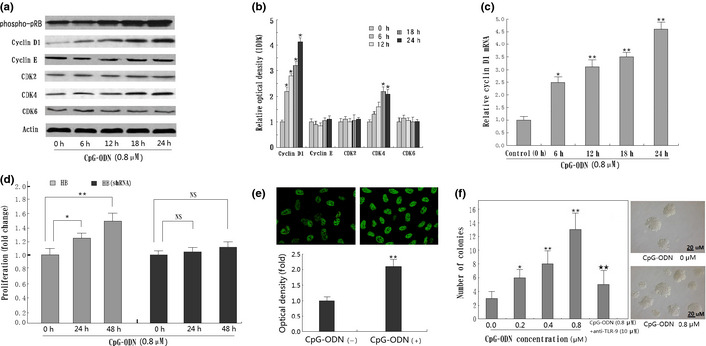
CpG‐oligonucleotides (CpG‐ODN) increase cyclin D1 expression as well as colony formation in HB cells. (a) Western blot for cyclin D1, cyclin E, cyclin‐dependent kinase (CDK)2, CDK4, CDK6, and phospho‐pRB using lysates from HB cells treated with 0.8 μM CpG‐ODN for the indicated time periods (0–24 h). Immunoblotting for each protein was done three times or more using independently prepared lysates, with similar results. (b) Changes in protein levels compared with control as determined by densitometric scanning of the immunoreactive bands. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (c) Detection of cyclin D1 mRNA by quantitative RT‐PCR in CpG‐ODN‐treated HB cells. Result shows CpG‐ODN treatment increased the cyclin D1 transcriptive level in a time‐dependent manner. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, compared to the non‐treatment group. (d) Blockage of cyclin D1 expression by RNA interference can significantly abolish the effects of CpG‐ODN treatment in HB cells. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. NS, not significant. (e) Detection of cyclin D1 protein in HB cells nuclear by confocal microscope. Semiquantitative analysis based on optical density shows significantly increased cyclin D1 in CpG‐ODN‐treated HB cells than in the non‐treatment group. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (f) Colony formation of HB cells treated with various concentrations of CpG‐ODN (0–0.8 μM) for 24 h. Results shown are the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. TLR‐9, Toll‐like receptor‐9. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, compared with panel 1 (0 μM CpG‐ODN). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, compared with panel 4 (0.8 μM CpG‐ODN).
