Figure 3.
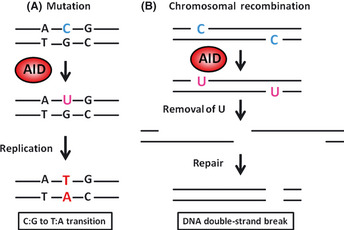
Molecular mechanisms of the induction of mutation and chromosomal recombination by activation‐induced cytidine deaminase (AID). (A) AID acts on single‐strand DNA during the transcriptional stage. AID binds to the target DNA and deaminates deoxycytidine (dC) to deoxyuracil (U), creating a U–G mismatch. The general DNA replication without repair pathways can convert U to T and G to A, generating C:G to T:A mutations. (B) DNA double‐strand breaks are generated through the repair process of AID‐induced U:G mismatches through the production of abasic sites. Class‐switch recombination (CSR) occurs by recombination of double‐strand breaks.
