Figure 4.
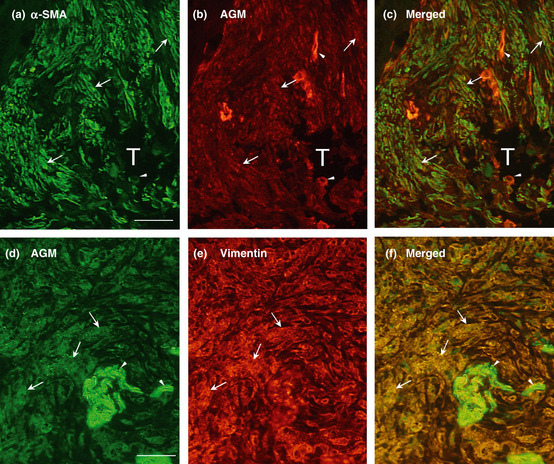
Double immunofluorescence staining of cancer tissues for angiomodulin (AGM) and α‐smooth muscle actin (α‐SMA) or vimentin. (a) A section of colon adenocarcinoma, which derived from a tumor specimens different from those used in Fig. 1, was subjected to double immunofluorescence staining with a rabbit anti‐α‐SMA polyclonal antibody (a: green) and the anti‐AGM monoclonal antibody (clone 88) for AGM (b; red) as described in Materials and Methods. The two images (a and b) were merged in (c). (d–f) A section of lung adenocarcinoma, different from the tumor specimens used in Fig. 1, was immunostained with a goat anti‐AGM polyclonal antibody (d; green) and a mouse anti‐vimentin monoclonal antibody (e; red). The two images (d and e) were merged in (f). Arrowheads, positive signals for AGM in blood vessels; arrows, positive signals for AGM, α‐SMA or vimentin in stromal tissues; T, tumor cell mass. Scale bar, 50 μm.
