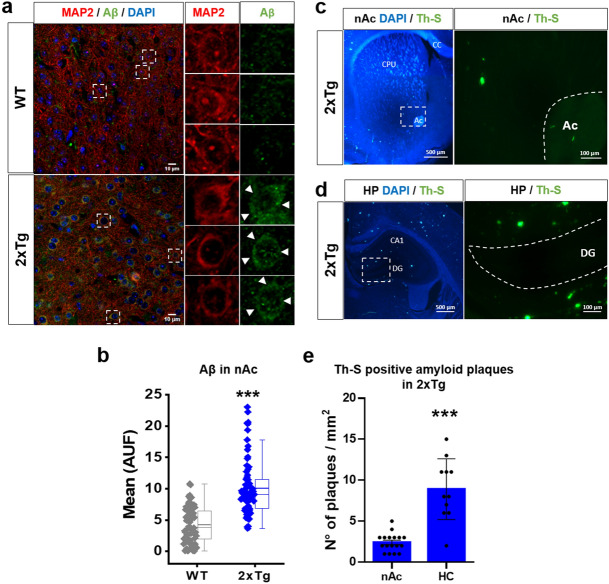
Figure 1.
Presence of amyloid pathology in the nAc of 2xTg mouse: (a) Immunohistochemistry of coronal slices (30 μm) and high magnification image (inset) showing Aβ in the nAc of 6 months old wild type (WT) and 2xTg mice. Aβ was detected using the MOAB2 antibody. (b) Quantification of Aβ fluorescence intensity of WT and 2xTg mice in the soma of nAc neurons (AFU: Arbitrary Fluorescence Units). In 2xTg mice Aβ fluorescence intensity was significantly increased. Data are mean ± SEM and each data point reflects one soma *** p < 0.0001. n = 3 WT and 3 2xTg. (c, d), Presence of amyloid plaques stained with Thioflavin S (Th-S) in the nAc (c) and compared with hippocampus (HC) (d) of 6 months old 2xtg mice (DAPI staining in blue). Inset shows high magnification. CC: corpus callosum; CPU: caudate-putamen; AC: anterior commissure; CA1: subfield of Cornu Ammonis; DG: dentate gyrus. (e), Quantification of the number of Th-S-Aβ plaques in nAc and HC. Data are mean ± SEM. (t(11.20) = 5.658, p = 0.0001). n = 3 WT and 3 2xTg. Images of nAc are located ventral and medial to the anterior commissure (not shown). Mann–Whitney test for (b), unpaired Student’s t-test with Welch correction for (e). Images were analyzed with ‘ImageJ’ 1.8.0_112 (NIH), https://imagej.nih.gov/ij.