Figure 1.
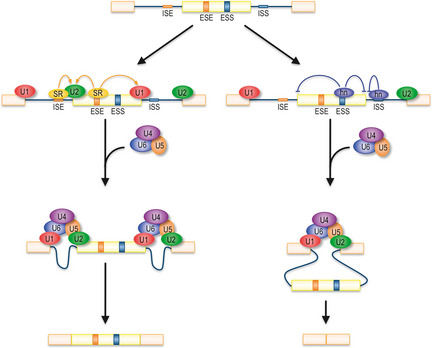
Schematic representation of mRNA splicing. U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle (snRNP) and U2 snRNP recognize 5′ splice site (5′ ss) and branch point sequence, respectively. U4/U6•U5 snRNP joining is followed by conformational changes to become the catalytically active spliceosome. Binding of SR proteins to exonic or intronic splicing enhancers (ESE and ISE, respectively) stimulates splicing efficiency, while binding of hnRNP to splicing silencers (ESS and ISS) suppresses splicing and causes exon skipping.
