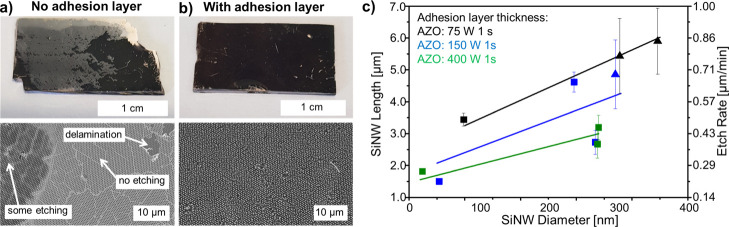
Figure 2.
MACE with and without the adhesion layer. (a,b) Top row: Large-scale photographs. Bottom row: Secondary electron SEM images. (a) Substrate after MACE without the adhesion layer. Inhomogeneous etching due to the bad contact between the Si and Au leads to film delamination or no etching in large areas. (b) Utilization of an aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) adhesion layer improves the contact and homogeneous etching. (c) Etch rate as a function of wire diameter for three different AZO thicknesses: the AZO layer was deposited during 1 s at 75 W (black symbols), 150 W (blue symbols), and 400 W (green symbols). The SiNW length and etch rate decrease for thicker adhesion layers. The lines are linear fits. Pitch: 590 nm; Au: 200 s 40 mA; MACE etchant composition 10:1:10 HF/H2O2/H2O etched during 7 min. Samples showing regions where the gold film was fractured are shown as triangles. Samples with a stable flat gold film are shown as squares.