Figure 3.
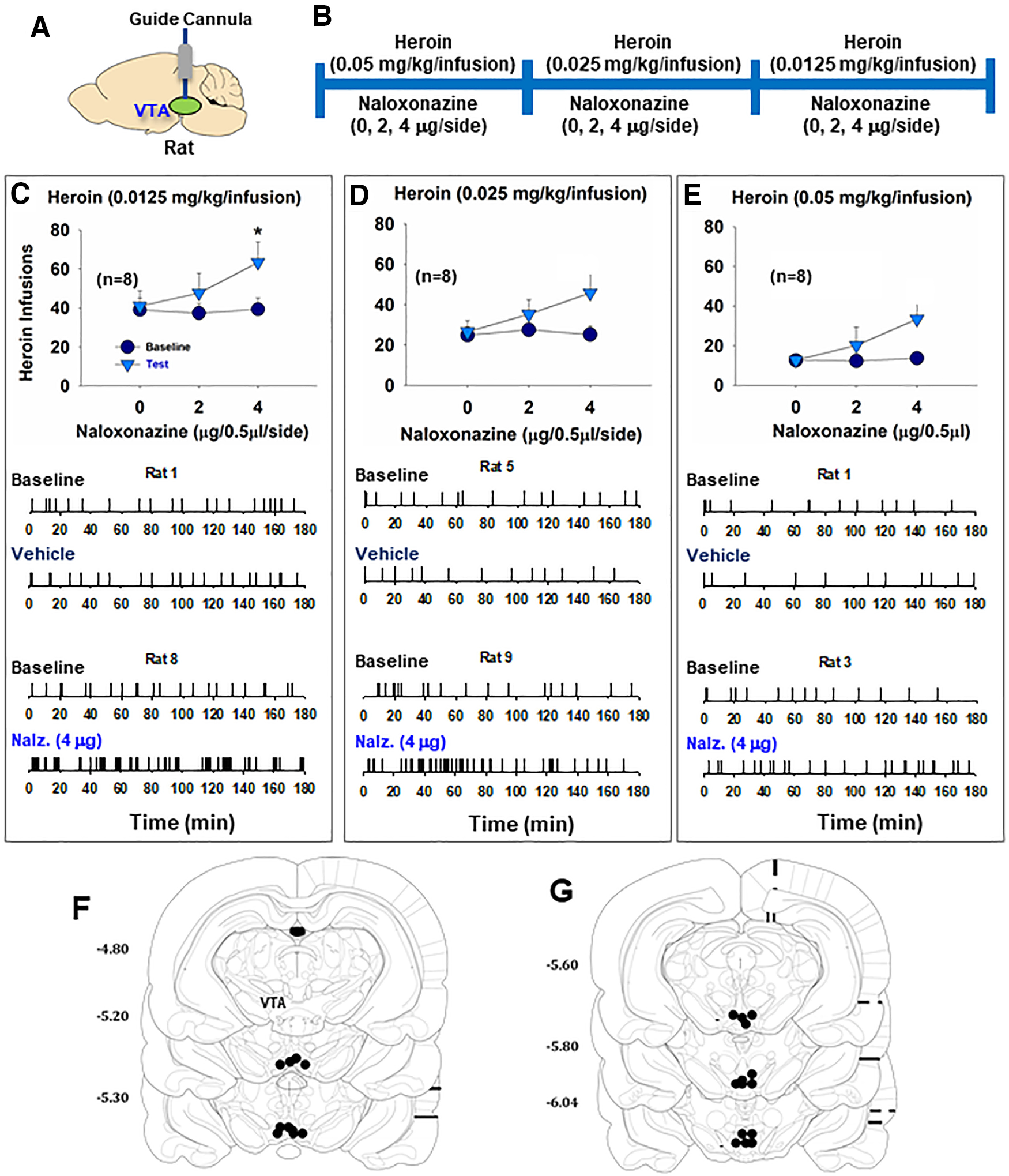
The effects of VTA MOR blockade on heroin self-administration in rats. A, B, General experimental procedures. C-E, Intra-VTA microinjections of naloxonazine increased the total numbers of heroin infusions. Statistically significant increases in self-administration were observed with the 0.0125 mg/kg dose of heroin (C), but not with the 0.025 mg/kg/infusion (D) or 0.05 mg/kg/infusion (E). Bottom panels, Representative event records of heroin infusions during a 3 h session from individual rats, illustrating higher rates of heroin self-administration and an evenly distributed pattern of heroin self-administration, suggesting a compensatory response in drug intake due to a reduction in heroin reward following MOR blockade (n = 8 in each group). F, G, Postexperimental histology illustrating microinjection loci in the VTA in rats. *p < 0.05 compared to baseline.
