Figure 7.
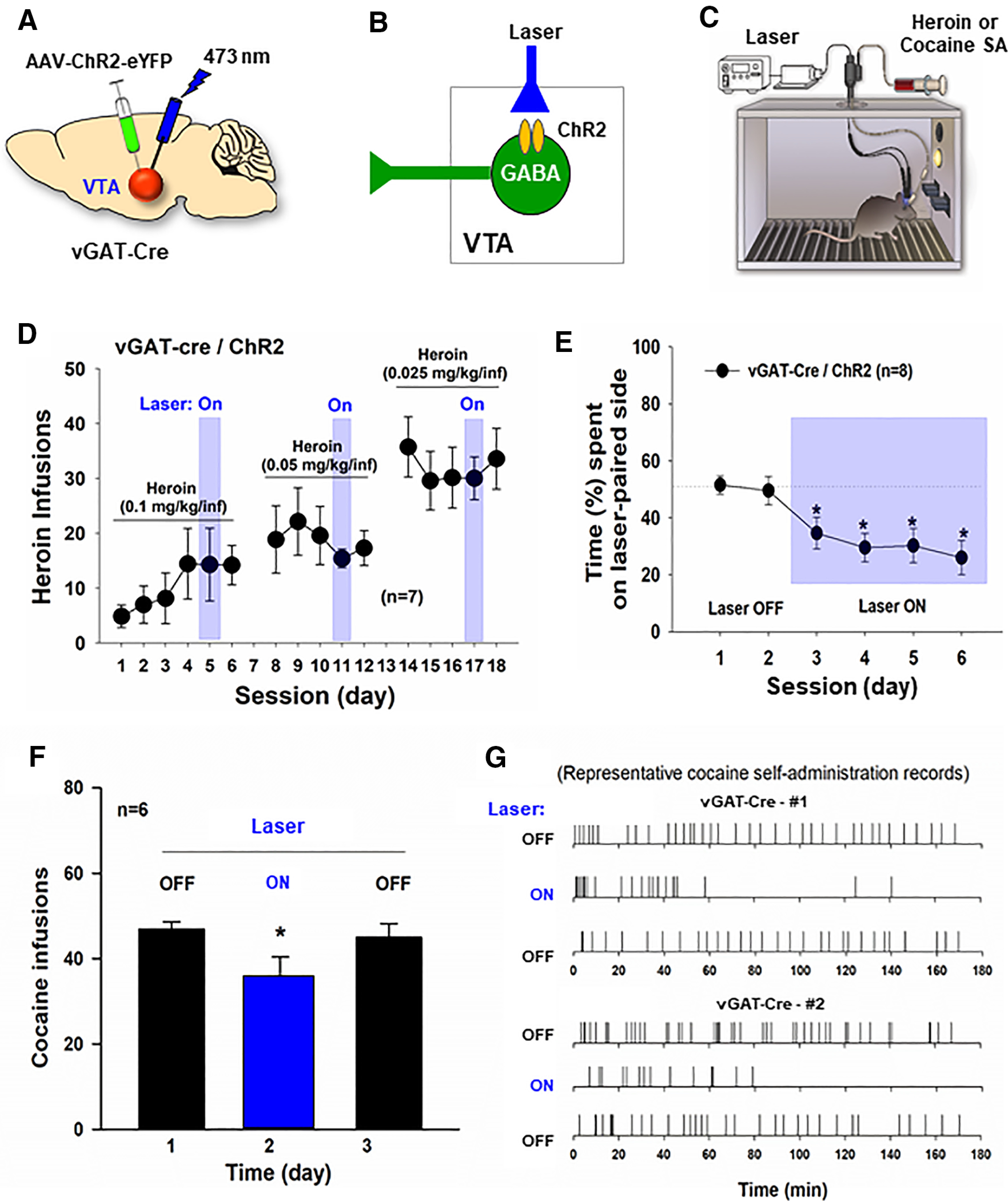
The effects of optogenetic modulation of VTA GABA neurons on heroin or cocaine self-administration. A–C, General experimental procedures. D, Response-contingent optical activation of VTA GABA neurons failed to alter intravenous heroin self-administration in vGAT-cre mice (n = 7) after stable self-administration was achieved. E, Optical activation of VTA GABA neurons is aversive, as assessed by RTPP. vGAT-cre mice with ChR2 expression in VTA GABA neurons (n = 10) spent less time in laser-paired compartment. F, Response-contingent optical activation of VTA GABA neurons inhibited intravenous cocaine self-administration in vGAT-cre mice. G, Representative cocaine self-administration records from 2 vGAT-cre mice, indicating that response-contingent optical activation of VTA GABA neurons inhibited cocaine self-administration. *p < 0.05 as compared to the baseline or Laser Off conditions.
