Figure 3.
Consequences of ATGL Deletion and Inhibition in the Heart
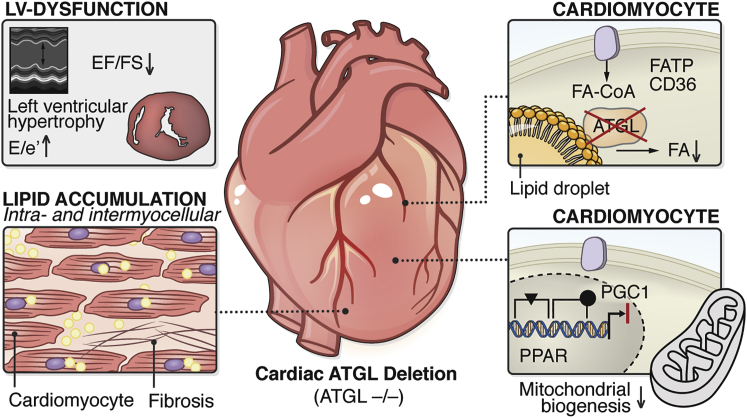
Cardiac-specific deletion and inhibition of ATGL results in systolic and diastolic LV dysfunction, LV hypertrophy (upper left box), cardiac lipid accumulation (lower left box), reduced cardiomyocytic lipolysis with lower cellular FA levels (upper right box), decreased ligand (FA)-induced PPARα/δ activation/reduced PGC-1 expression, and reduced mitochondrial biogenesis/mitochondrial dysfunction (lower right box).
CD36, cluster of differentiation 36 (also known as fatty acid translocase); e′, tissue Doppler-passive LV filling; E-wave (early passive LV filling); EF, ejection fraction; FA-CoA, fatty acyl-CoA ester; FATP, fatty acid transport protein; FS, fractional shortening; LV, left ventricular; PGC1, PPARγ coactivator-1; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor.