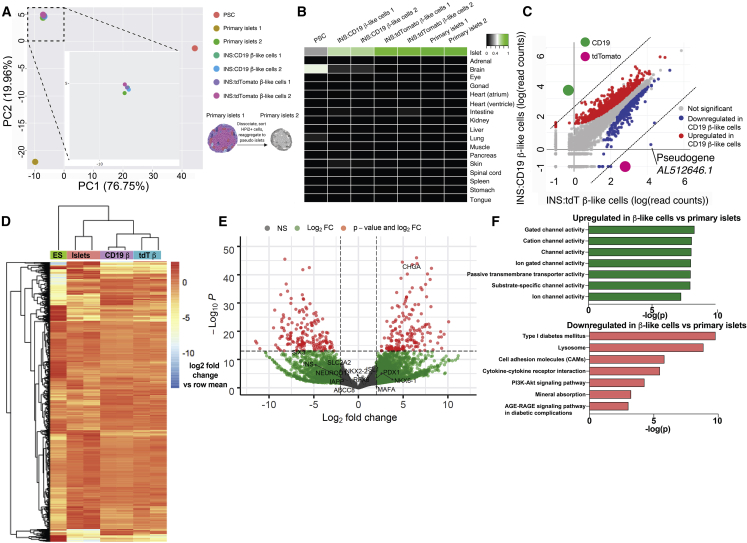
Figure 2.
Gene Expression of β-like Cells Differentiated from INS:tdT and INS:CD19 PSCs
(A) Principal-component analysis (PCA) of undifferentiated human pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), CD19-expressing β-like cells (INS:CD19 β-like cells 1 and 2), tdTomato-expressing β-like cells (INS:tdTomato β-like cells 1 and 2), and human primary islets. Primary islet 1 RNA was extracted from primary islets, and primary islet 2 RNA was extracted from pseudoislets reaggregated from sorted endocrine cells. The boxed area was magnified for better sample separation.
(B) Keygene plots of RNA-seq samples, showing islet identity of tdTomato- and CD19-expressing β-like cells and primary islets but not for PSCs.
(C) Scatterplot of log10 (read counts) values for transcripts present in tdTomato-expressing β-like cells (x axis) and CD19-expressing β-like cells (y axis). The most differentially expressed genes, CD19 and tdTomato, are labeled in green and magenta, respectively.
(D) Heatmap and hierarchical clustering of the approximately 1,500 most differentially expressed genes between ESCs, primary islets, and β-like INS reporter cells.
(E) Volcano plot showing genes differentially expressed in β-like cells (right) and in primary islets (left). Genes with a log2 fold change of more than 2 and p < 10−14 are shown in red.
(F) Selected KEGG pathways enriched in genes upregulated in β-like cells compared with primary islets (green) and in genes downregulated in β-like cells compared with primary islets (red).
See also Figures S2 and S3 and Tables S1 and S2.