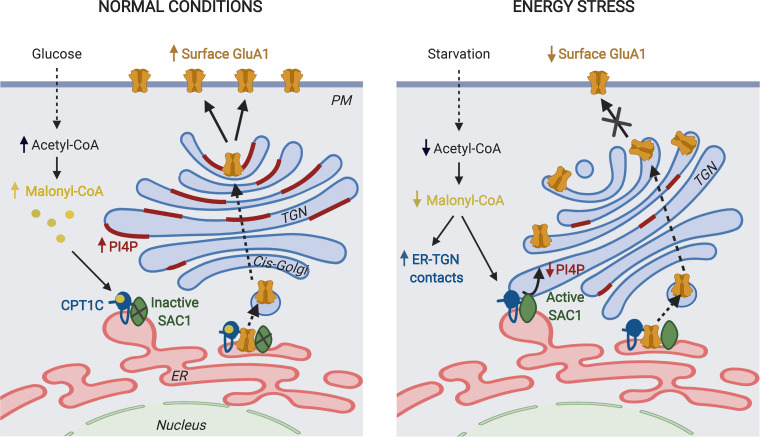
Figure 10.
A working model for CPT1C regulation of GluA1 trafficking. CPT1C and SAC1 form part of the AMPAR complex at the ER of neurons. We do not discard the existence of CPT1C/SAC1 pairs in the ER that do not form part of AMPAR complexes. In normal nutrient conditions, malonyl-CoA–bound CPT1C down-regulates SAC1 activity, allowing the accumulation of PI(4)P at the TGN. This favors the trafficking of GluA1-containing AMPARs from the TGN to the PM through the secretory pathway. In energy stress conditions that decrease malonyl-CoA levels, such as glucose deficiency, ER-TGN contacts are increased and CPT1C favors the transport of SAC1 to these junctions. At the same time, malonyl-CoA–free CPT1C releases its inhibition on SAC1 activity. This results in dephosphorylation of PI(4)P at the TGN by SAC1 in trans, which halts GluA1-containing AMPAR trafficking. The figure was drawn using BioRender web-based software.