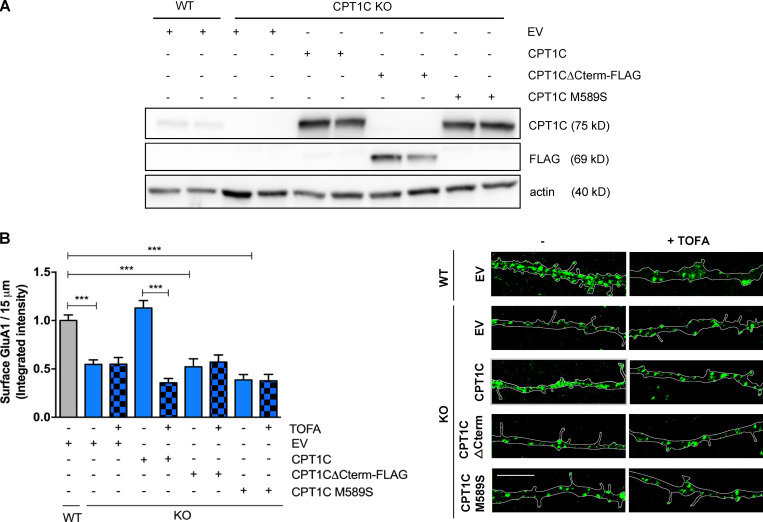
Figure 3.
CPT1C C-terminal and binding to malonyl-CoA are needed to regulate GluA1 trafficking. (A and B) Surface GluA1 level recovery by CPT1C reexpression in KO neurons. CPT1C KO cortical neurons were transduced at 7 DIV with lentiviral vectors carrying CPT1C, CPT1CM589S, CPT1CΔCterm-FLAG, or an EV. WT neurons transduced with the EV were used as the control. At 14-15 DIV, cells were treated with TOFA (20 µg/ml, 2 h) or the vehicle (DMSO; 1:500). Surface GluA1 levels were detected and quantified as in Fig. 1. Proper overexpression of different CPT1C forms was corroborated by Western blot in A. Data in B represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments performed by biological duplicates (one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s comparison test; ***, P < 0.001). WT + EV + vehicle (1.00 ± 0.02, n = 17), KO + EV + vehicle (0.55 ± 0.05, n = 80), KO + EV + TOFA (0.54 ± 0.069, n = 63), KO + CPT1C + vehicle (1.13 ± 0.07, n = 85), KO + CPT1C + TOFA (0.35 ± 0.04, n = 68), KO + CPT1CΔCterm-FLAG + vehicle (0.52 ± 0.08, n = 54), KO + CPT1CΔCterm-FLAG + TOFA (0.57 ± 0.07, n = 56), KO + CPT1CM589S + vehicle (0.38 ± 0.05, n = 52), and KO + CPT1CM589S + TOFA (0.38 ± 0.07, n = 33). Scale bars = 5 µm.