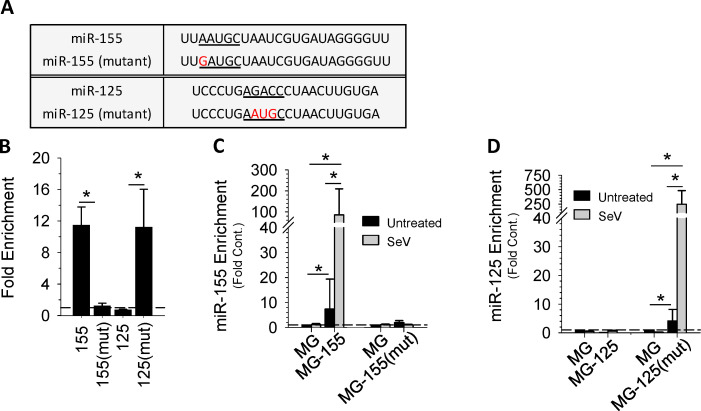
Figure 4.
cRILP, FMR1, and miRNA motifs. (A) Schematic view of wild-type and mutant miRs showing the cRILP-associated motif (underlined) and mutations (in red). (B) RIP/chromatin immunoprecipitation of FMR1-associated miRNAs. HeLa cells were cotransfected with HA-Flag-FMR1 and the specified miRNA. FMR1 was immunoprecipitated, and qPCR analysis of the eluted miRNAs shows that FMR1 binds to the cRILP miR, miR-155. Mutation of the AAUGC motif abolishes this binding. Placing this motif into miR-125 enables its binding to FMR1. (C and D) Sequence specificity and exosomal miR loading. HeLa cells were transfected with the empty vector (MG) or the specified miRNA. After inflammasome activation by SeV, miR content in the exosomes was determined by qPCR. Wild-type miR-155 is enriched within the exosome in an inflammasome-mediated manner, while its mutant is not. miR-125 is not present in inflammasome-induced exosomes; however, the mutant miR-125 containing the AAUGC motif is selected for secretion within the exosome. Data are shown as mean ± SD; *, P ≤ 0.05 for n = 4–8.