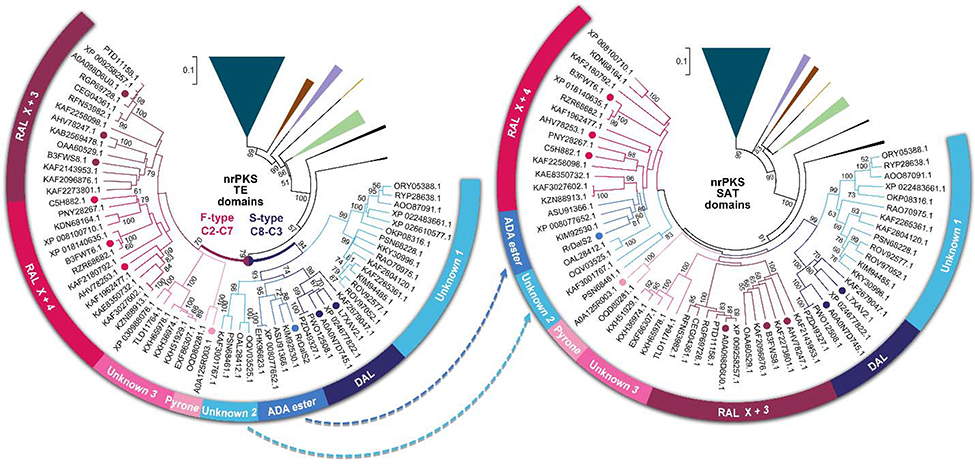
Figure 4. Phylogenetic trees for nrPKS TE and SAT domains.
nrPKSs with O-C bond-forming Type I TEs were collected from NCBI GenBank in a comprehensive search (>40% amino acid identity, >80% coverage to “bait” sequences), aligned using MEGA 7, and their evolutionary histories were inferred with the neighbor joining method. nrPKSs with thioesterase/Claisen cyclase domains were used as the outgroup (dark teal triangle). The percentage (if >50%) of replicate trees where the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. Branches basal to BDL synthases were collapsed and shown as colored wedges (brown, collaborating hrPKS – nrPKS systems with a discrete TE protein; purple, TEs from orsellinic acid hybrid metabolite synthases; yellow, polylactone TEs; green, TEs from orsellinic acid synthases; black, TEs from synthases with unknown products). Colored dots represent TEs from voucher BDL synthase systems (maroon, zearalenone,51 lasiodiplodin19 and hypothemycin52 synthases; red, resorcylide19 and monocillin II18,52 synthases; pink, cladosporin53 synthase; blue, RrDalS2, navy, dehydrocurvularin20,54 synthases). Blue arrows indicate the relocation of the ADA ester and the unknown S-type clade into the RAL X+4 clade.