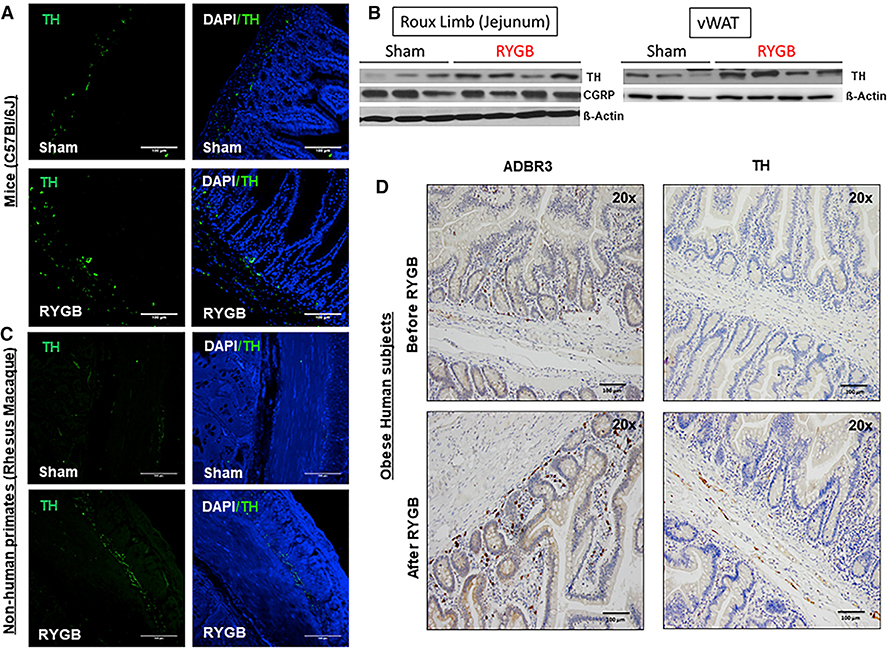
Figure 2. RYGB Induces an Increase in Markers of Gut’s Sympathetic Nerve Activity.
(A) TH expression—assessed by immunofluorescence (IF)—in the Roux limb (or jejunum) of DIO C57BL/6 mice after RYGB compared with their sham counterparts 6 weeks after surgery. Sham n = 5, RYGB n = 5.
(B) TH and CGRP expression—assessed by western blot—within the Roux limb (jejunum) as well as TH expression within vWAT of RYGB- and sham-operated DIO mice 6 weeks after surgery. β-Actin serviced as a loading control.
(C) TH expression—assessed by IF—in the Roux limb (or jejunum) of DIO rhesus macaque monkeys after RYGB compared with their sham counterparts 12 weeks after surgery. Sham n = 4, RYGB n = 4.
(D) ADBR3 and TH expression in Roux (or proximal jejunum)—assessed by IHC—of obese human subjects at time of surgery (before RYGB) and 1–5 years afterward (after RYGB). n = 4–5. Scale bar, 100 μm (A, C, and D).