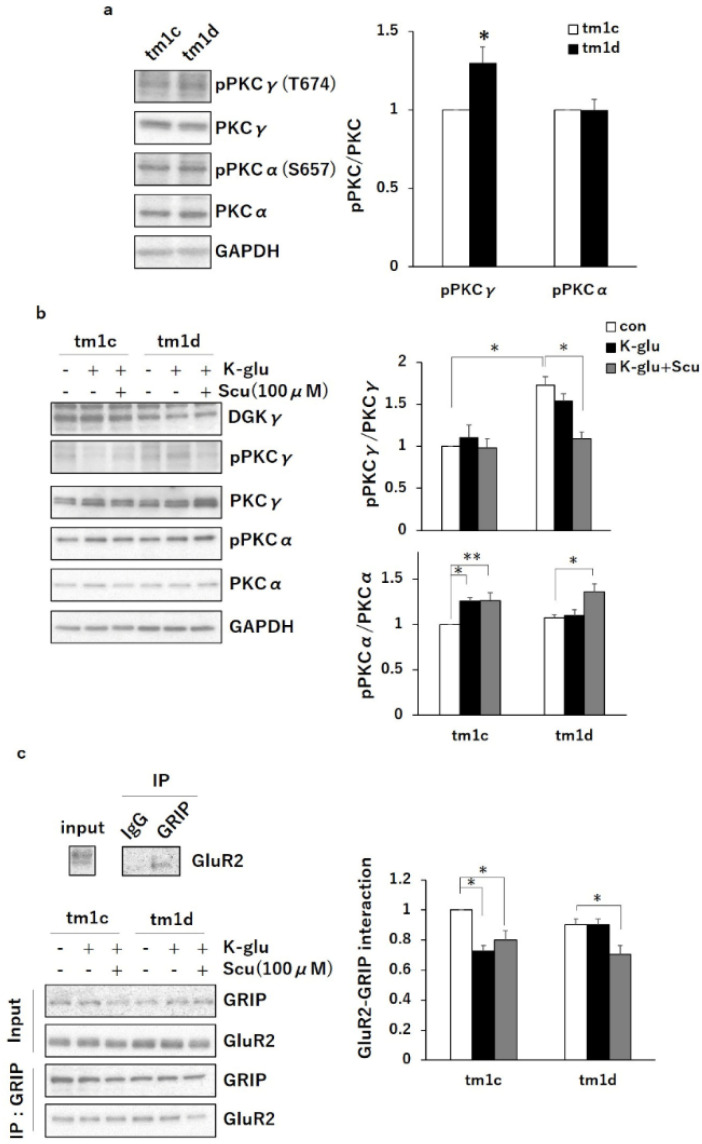
Figure 3.
Protein kinase C α (PKCα) inactivation during long-term depression (LTD)-induced stimulation by K-glu in tm1d mice: (a) cerebellar lysates from tm1c and tm1d mice were subjected to Western blotting and probed with anti-PKCγ, anti-PKCα, anti-phospho-PKCγ, anti-phospho-PKCα, and anti-GAPDH antibodies. Quantification of the autophosphorylation of PKCγ and PKCα was performed by ImageJ. The phosphorylation levels of PKCγ and PKCα were normalized to the PKCγ and PKCα expression levels. The ratio of phosphorylation of PKCγ and PKCα to the expression levels of PKCγ and PKCα to tm1c was plotted (PKCγ: n = 3; PKCα: n = 3); * p < 0.05, followed by Student’s t-test. (b) Acute cerebellar slices from tm1c and tm1d mice were incubated with or without Scu (100 µm) for 1 h and subsequently were treated with K-glu (50 mM KCl + 100 µM L-glutamate) for 5 min. Lysates from the slices were subjected to Western blotting and probed with anti-DGKγ, anti-phospho-PKCγ, anti-PKCγ, anti-phospho-PKCα, anti-PKCα, and anti-GAPDH antibodies. Quantification of the autophosphorylation of PKCγ and PKCα was performed by ImageJ. The phosphorylation levels of PKCγ and PKCα were normalized to the PKCγ and PKCα expression levels. The ratio of phosphorylation of PKCγ and PKCα to the control (con) in tm1c was plotted (n = 6); * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (c) The lysates after K-glu treatment were immunoprecipitated using anti-glutamate receptor interacting protein (GRIP) antibody. The immunoprecipitates were subjected to western blotting and probed with anti-GRIP and anti-GluR2 antibodies. IgG (anti-transient receptor potential cation channel type 3 (TRPC3) antibody) was used as a control. Quantification of co-immunoprecipitated GluR2 was performed by ImageJ and was normalized to the input level of GluR2. The ratio of the co-immunoprecipitated GluR2 to the control (con) in tm1c was plotted (n = 6); * p < 0.05, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Con means control.