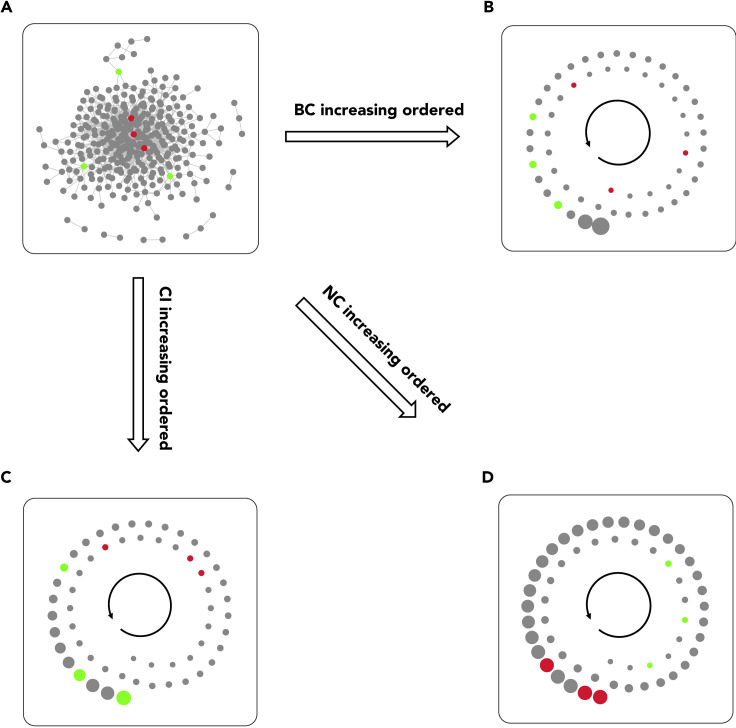
Figure 3.
The Positional Bias of Betweenness Centrality and Collective Influence
This network has been reconstructed using the interactions presented by the STRING database and based on genes in the blue module provided by Xia et al.38 according to the weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) as seed proteins. Red nodes are three examples of nodes with a high number of connections positioned in the center of the network; green nodes are representative of nodes with a lower number of connections at the edges of the network. A module of interacting nodes, including all red and green ones, was extracted from the entire network for the visualization of (B)–(D) in the spiral layout. Also, for simplicity and clear visualization, node connections are not shown in (B)–(D).
(A) The entire protein-protein interaction network of adrenocortical carcinoma. The nodes were automatically organized using the Inverted Self-Organizing Map Layout with some slight alterations to make the selected nodes visible.
(B) The vertices of extracted module ordered based on their betweenness centrality values.
(C) The vertices of extracted module ordered based on their collective influence values.
(D) The vertices of extracted module ordered based on their neighborhood connectivity values.
The network was analyzed by the influential R package and illustrated using the Cytoscape software. BC, CI, and NC represent betweenness centrality, collective influence, and neighborhood connectivity, respectively.