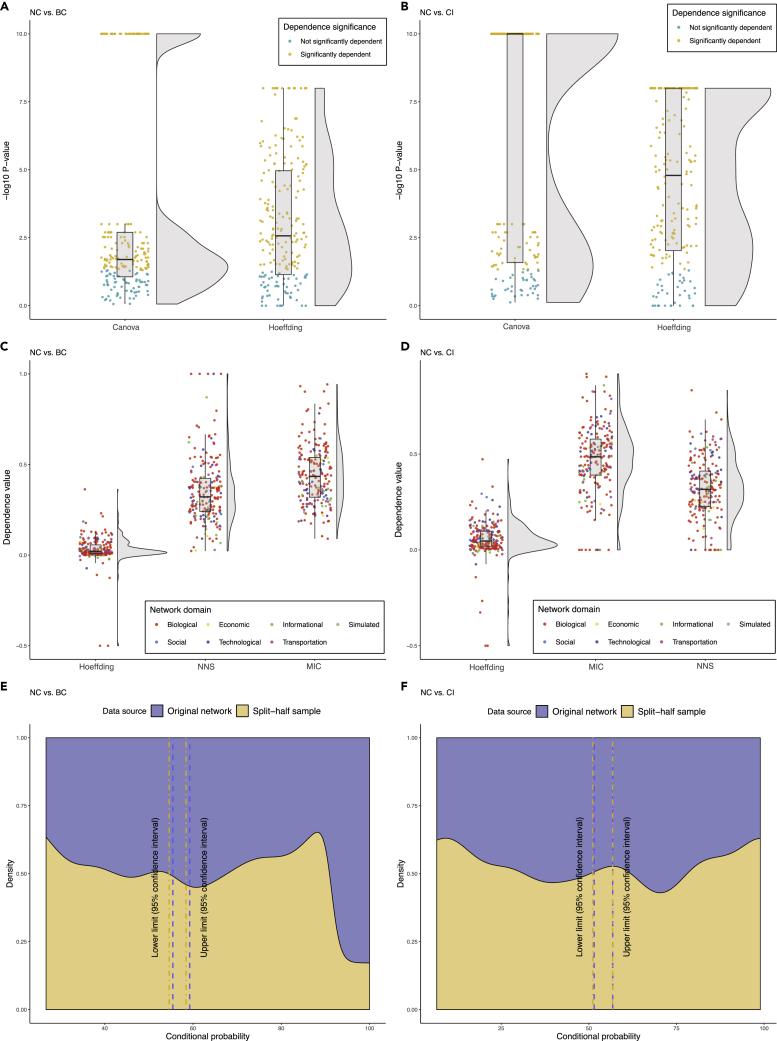
Figure 4.
The Association of Betweenness Centrality/Collective Influence, and Neighborhood Connectivity in 200 Networks
(A) Statistical significance of the dependence of betweenness centrality on neighborhood connectivity based on two different dependence tests, including CANOVA and Hoeffding across all networks.
(B) Statistical significance of the dependence of collective influence on neighborhood connectivity based on two different dependence tests, including CANOVA and Hoeffding across all networks.
(C) Descriptive dependence of betweenness centrality on neighborhood connectivity based on three different tests, including Hoeffding, MIC, and NNS across all networks.
(D) Descriptive dependence of collective influence on neighborhood connectivity based on three different tests, including Hoeffding, MIC, and NNS across all networks.
(E) The conditional probability of deviation of betweenness centrality from its mean given that neighborhood connectivity has deviated from its corresponding mean in the opposite direction based on both original networks as well as their split-half random samples.
(F) The conditional probability of deviation of collective influence from its mean given that neighborhood connectivity has deviated from its corresponding mean in the opposite direction based on both original networks as well as their split-half random samples.
BC, CI, NC, Canova, NNS, and MIC represent betweenness centrality, collective influence, neighborhood connectivity, continuous analysis of variance, non-linear non-parametric statistic, and maximum information coefficient, respectively.