Figure 2. Distribution of trials according to methodological and reporting quality assessments that might impair the outcomes of the trial.
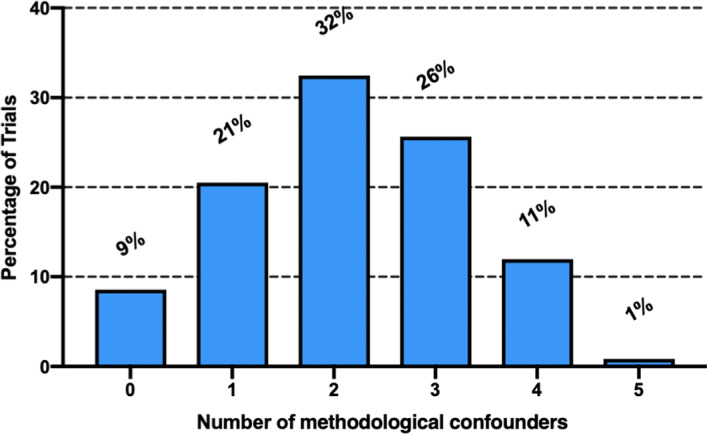
Distribution of trials according to the number of methodological and reporting quality characteristics (methodological confounders) they possess after the assessment: 9% of the trials had none of the methodological confounders (n=10), 21% of the trials possessed 1 methodological confounder (n=24), 32% of the trials possessed 2 major methodological confounders (n=38), and 26% of the trials possessed 3 major methodological confounders (n=30). In addition, 12% of the trials had >3 methodological confounders. This list of methodological confounders analyzed included the following: (1) inadequate allocation sequence concealment, (2) no blinding of patients, (3) early stop of trial, (4) not using intention‐to‐treat analysis, (5) absence of protocol, and (6) no explicit statement about status of loss to follow‐up.
