Figure 4. Sorbs2 (sorbin and SH3 domain‐containing 2) deficiency leads to cardiac arrhythmia.
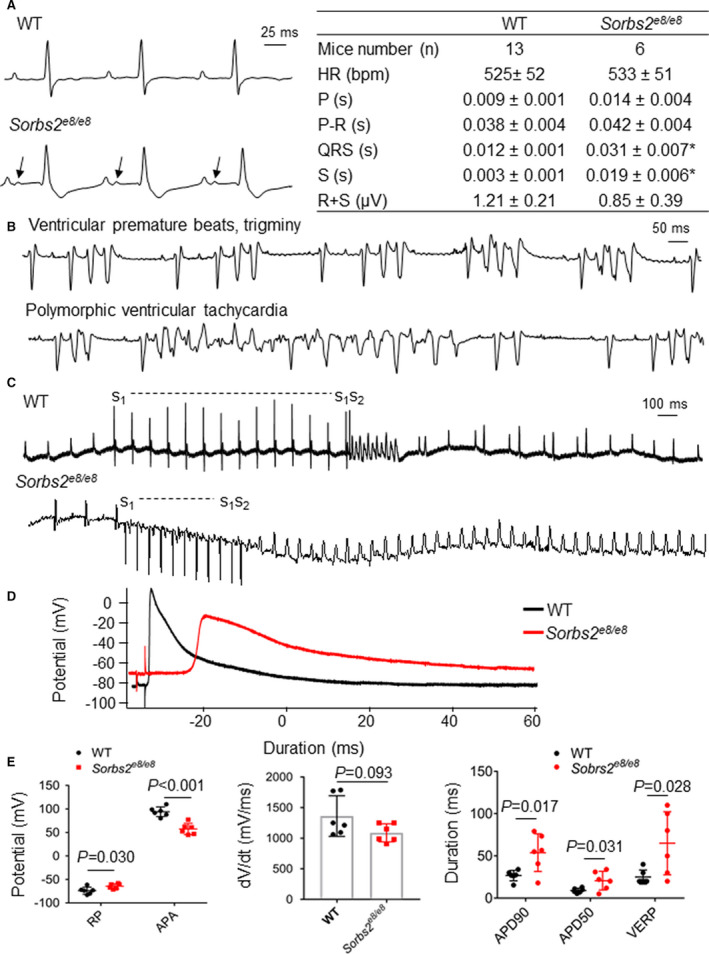
A, Shown are surface ECGs and quantification analysis in 4‐month‐old wild‐type (WT) and Sorbs2e8/e8 mice. N=6 to 13. Unpaired 2‐tailed Student t test. *P<0.05. B, Ventricular premature beats and trigeminy (top) and polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT) (bottom) were recorded in Sorbs2e8/e8 mice. C, Induction of nonsustained VT in Langendorff‐perfused WT mouse heart by programmed electrical stimulation (s1‐s1=100 ms, s1‐s2=30 ms) (top); induction of sustained monomorphic VTs in Langendorff‐perfused Sorbs2e8/e8 mouse heart by programmed stimulation (s1‐s1=100 ms, s1‐s2=80 ms) (bottom). D, Representative action potentials were recorded from the endocardial surface of isolated right ventricles (RVs) of Sorbs2e8/e8 and WT mice at a pacing cycle length of 200 ms. E, Compared with WT mice, Sorbs2e8/e8 mice RV action potentials have depolarized resting potentials (RPs), decreased action potential amplitudes (APAs), reduced upstroke velocity at phase 0 (Vmax, maximal velocity), and prolonged action potential durations at 50% (APD50) and 90% (APD90) repolarization, as well as a lengthened ventricular effective refractory period (VERP). N=6. Unpaired 2‐tailed Student t test. Bpm indicates beats per minute; HR, heart rate; P, duration of P waves; P‐R, duration of PR interval; QRS, duration of QRS complex; R+S, QRS amplitude; and S, duration of S wave.
