Figure 1. Blood pressure (BP) and the risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD) incidence in men stratified by the use of antihypertensive treatment. HR indicates hazard ratio.
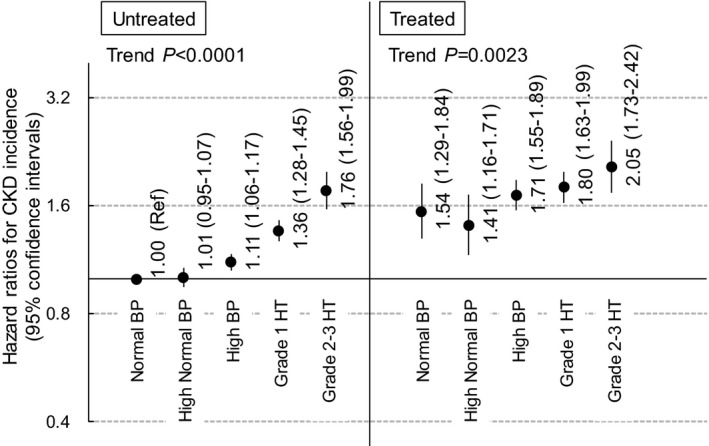
Covariates were age, body mass index <18.5 kg/m2, body mass index ≥25 kg/m2, current smoking status, alcohol consumption, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and estimated glomerular filtration rate at baseline.
