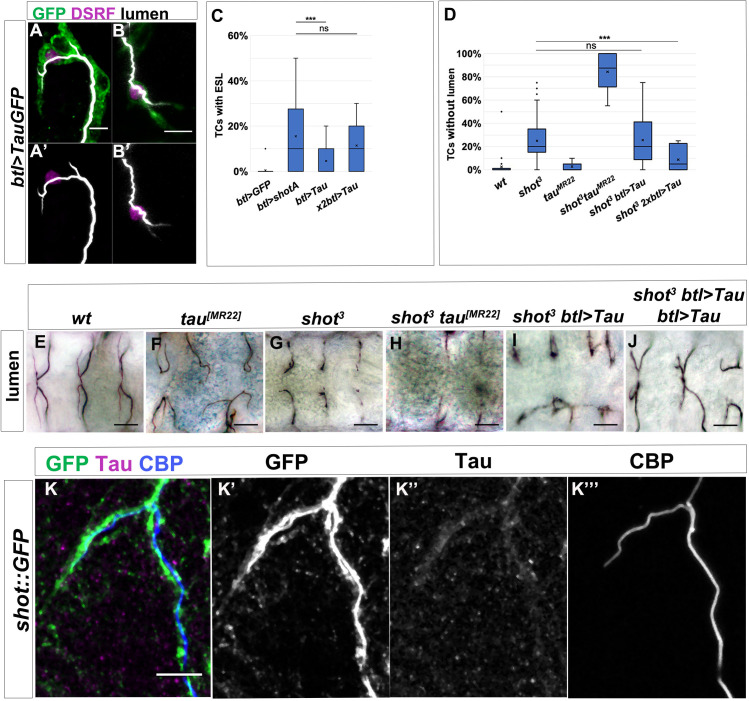
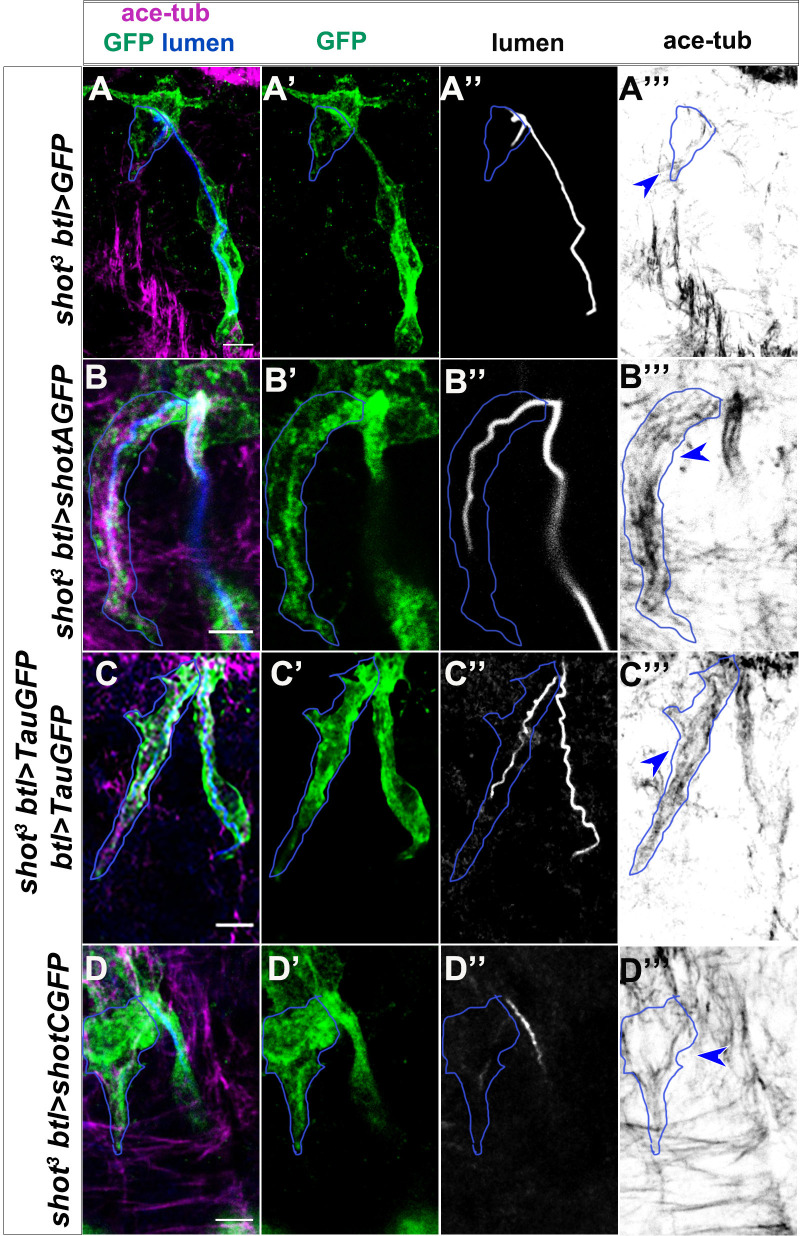
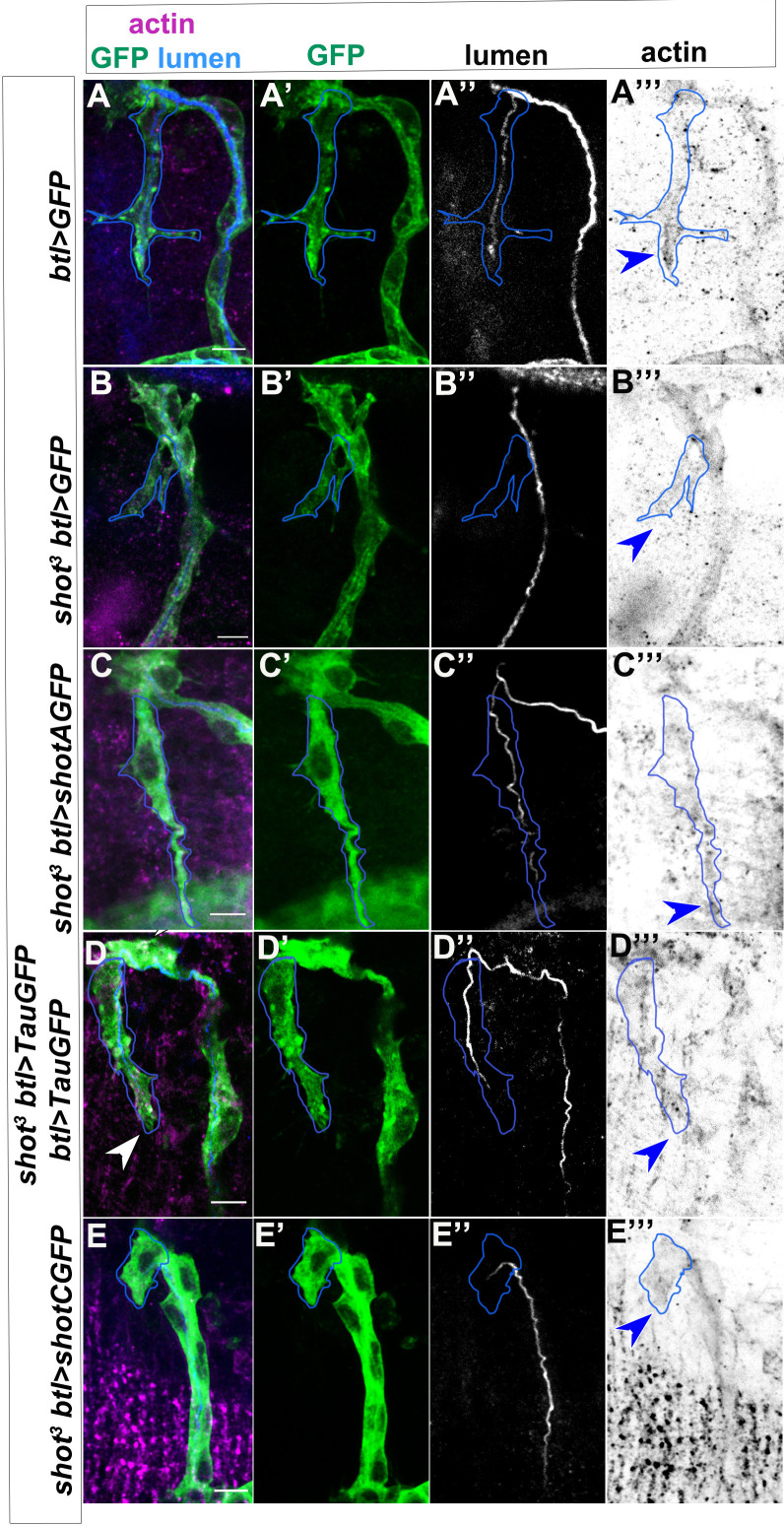
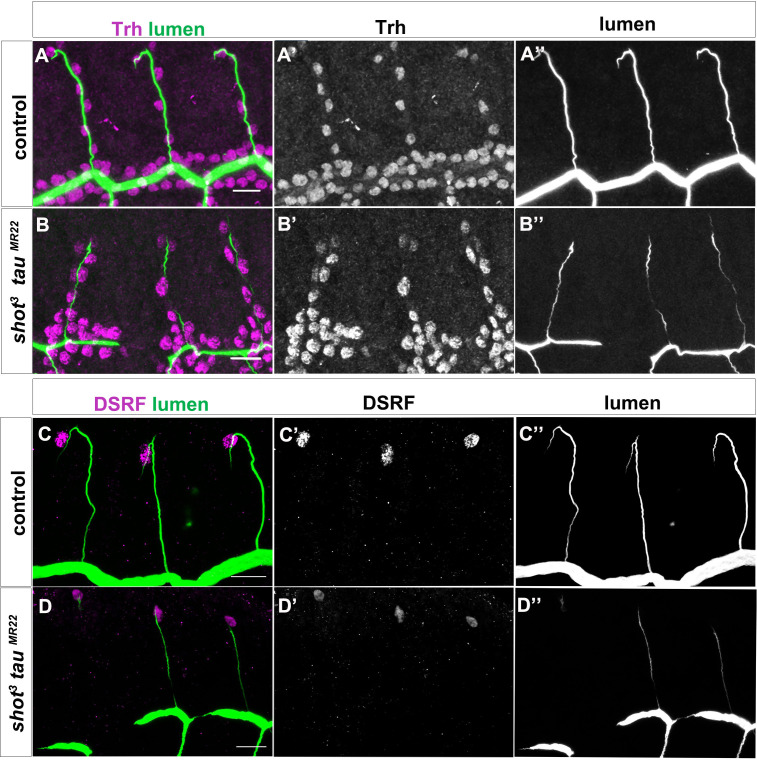
Figure 8. Shot and Tau functionally overlap during subcellular lumen formation.
(A–B) DB (A) and GB (B) embryonic TCs expressing tauGFP in the tracheal system, stained with GFP (green), CBP (white) and DSRF (magenta), showing the ESL phenotype induced by Tau overexpression. In A’ in B’ lumen and TC nuclei are shown, anterior side on the left, dorsal side is up; scale bar 5 μm. (C) Quantification of TCs with ESL in embryos overexpressing GFP (n = 240); ShotA (n = 400); one copy of btl >tauGFP (n = 440) or two copies of btl >tauGFP (n = 300). ***p-value<0.001; ns refers to a p-value>0.1. Statistics by two-tailed Student’s t-test. (D) Quantification of TCs without subcellular lumen in control (n = 820), shot3(n = 600), tau[MR22] (n = 180), shot3; tau[MR22](n = 180), shot3; btl >Tau (n = 440) and shot3; btl >Tau btl >Tau (n = 260) embryos. ***p-value<0.001; ns refers to a p-value>0.1. Statistics by two-tailed Student’s t-test. (E–J) Dorsal view of TCs from st. 16 embryos (genotype indicated) stained with anti-Gasp. tau deletion mutant does not display a subcellular lumen phenotype (D and F) but enhances the effect of shot mutation in the double mutant shot3; tau[MR22]. One copy of Tau is not sufficient to rescue shot3 (D and I, n = 400) but two copies rescues the shot LOF TC phenotype (D and J n = 260). Scale bars 10 µm. (K) Tau is detected in embryonic TCs. Embryonic shot::GFP dorsal TC stained with GFP (green in K, grey in K’), anti-Tau antibody (magenta in K, grey in K’) and CBP (blue in K grey in K’). Scale bar 5 μm.