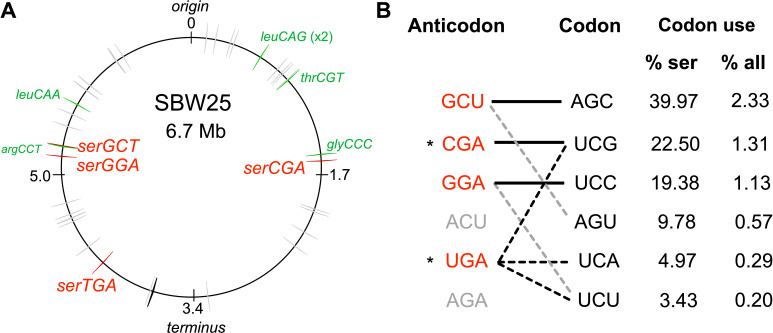
Figure 1. The tRNA gene set and serine translation system in P. fluorescens SBW25.
(A) Genomic location of the 66 canonical (grey arrows) and one non-canonical (cysGCA-2; black arrow) tRNA genes. Four tRNA genes encode seryl-tRNAs (red arrows). One of these, serCGA, is predicted to encode a non-essential tRNA type. Six other tRNA genes encoding the remaining five non-essential tRNA types (green arrows). Replication origin and terminus are indicated. (B) The predicted translational relationship between seryl-tRNAs and serine codons. The six theoretically possible seryl-tRNA anticodons are listed on the left (red = present in SBW25, grey = absent, * = theoretically capable of translating codon UCG), and six cognate codons are listed in column 2. Connections signify a theoretical match (solid black lines = Watson Crick pairing; black dotted lines = wobble pairing through post-transcriptional modification; grey dotted line = G:U wobble pairing). Columns 3 and 4 list codon use as a percentage of serine and all codons, respectively (Chan and Lowe, 2016). Anticodons and codons are 5'→3'.