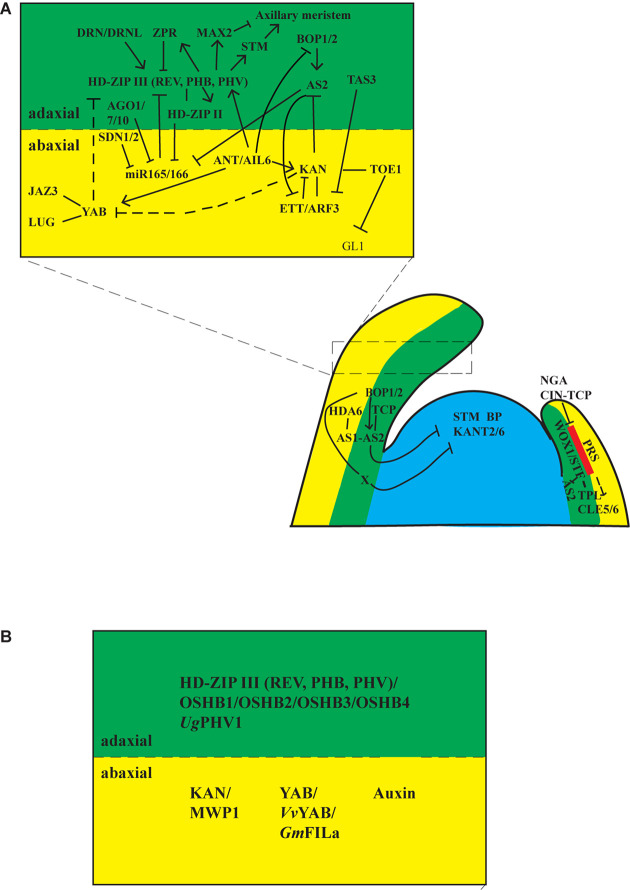
FIGURE 2.
Regulatory networks for establishing leaf polarities. (A) Gene regulatory networks in Arabidopsis. Upper, Gene regulatory networks for adaxial/abaxial polarity. Adaxial identity is established by HD-ZIP III transcription factors, whereas the abaxial identity is established by KAN and YAB transcription factors. The activities of HD-ZIP III are repressed by ZRP proteins and miR165/166. HD-ZIP III proteins activate and interact with HD-ZIP II transcription factors to repress expression of miR165/166; thus, a feedback loop is formed between miR165/166-HD-ZIP III-HD-ZIP II. miR165/166 are processed and sequestered by AGO1, AGL7, AGO10, and other miRNA processing proteins. SDN1 and SDN2 proteins mediate the degradation of miR165/166. A second feedback loop functions between AS2-KAN-ETT. ETT is repressed by TAS3, ETT physically interacts with KAN to repress AS2 and KAN, and AS2 represses ETT. AS2 also represses miR165/166. Thus, AS2 is a hub between these two feedback loops. KAN interacts directly with TOE1 to form a repressive loop at the GL1 locus to suppress abaxial trichome formation in juvenile leaves. DRN and DRNL bind to HD-ZIPIII proteins and assist them in activating STM and MAX2 to activate or suppress axillary meristem formation on the adaxial side of leaves. Lower, Gene regulatory networks for proximodistal and mediolateral polarities. Proximodistal polarity established by BOP1/2 and AS1/2 complexes. BOP1/2 proteins activate AS2 directly, and AS2 physically interacts with AS1 and TCP transcription factors. AS1 associates with HDA6 to restrict class I KNOX genes (STM, BP, KNAT2, and KNAT6) in the SAM to suppress meristematic activities in leaves. BOP1/2 proteins function through AS2-dependent and AS2-independent pathways to repress class I KNOX genes. WOX1 and PRS are expressed at the boundary between adaxial and abaxial domains. WOX1 and PRS are restricted from the tip of the leaf by NGS and CIN-TCP transcription factors. TPL physically interacts with STF (WOX1) to repress AS2 and promote lateral expansion of the lamina. CLE5 and CLE6 act downstream of WOX1 and PRS. Red area indicates the expression domain of WOX1 and PRS. Filled lines represent direct interaction and dashed lines indicate indirect or genetic interaction. (B) Conserved gene regulatory network among plants. Adaxial polarity is established by HD-ZIP III (REV, PHB, PHV) transcription factors. Orthologs of the HD-ZIP III transcription factors, OSHB1/2/3/4 in rice, and UgPHV1 in Utricularia have similar roles as HD-ZIP III transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Abaxial polarity is established by YAB, KAN, and auxin pathways in Arabidopsis. The KAN1 ortholog MWP1 in maize, the YAB ortholog VvYAB in grapevine, and GmFILa in soybean have conserved roles as the YAB proteins in Arabidopsis. How auxin is involved in establishing adaxial–abaxial polarity is complicated. Nevertheless, it is required for polarity establishment in Arabidopsis and Chinese cabbage.